- adware
- DDoS
- phishing
- social engineering
- spyware
2. What causes a buffer overflow?
- launching a security countermeasure to mitigate a Trojan horse
- downloading and installing too many software updates at one time
- attempting to write more data to a memory location than that location can hold
- sending too much information to two or more interfaces of the same device, thereby causing dropped packets
- sending repeated connections such as Telnet to a particular device, thus denying other data sources
3. Which objective of secure communications is achieved by encrypting data?
- authentication
- availability
- confidentiality
- integrity
4. What type of malware has the primary objective of spreading across the network?
- worm
- virus
- Trojan horse
- botnet
5. What commonly motivates cybercriminals to attack networks as compared to hactivists or state-sponsored hackers?
- financial gain
- fame seeking
- status among peers
- political reasons
6. Which type of hacker is motivated to protest against political and social issues?
- hacktivist
- cybercriminal
- script kiddie
- vulnerability broker
7. What is a ping sweep?
- a query and response protocol that identifies information about a domain, including the addresses that are assigned to that domain.
- a scanning technique that examines a range of TCP or UDP port numbers on a host to detect listening services.
- a software application that enables the capture of all network packets that are sent across a LAN.
- a network scanning technique that indicates the live hosts in a range of IP addresses.
8. In what type of attack is a cybercriminal attempting to prevent legitimate users from accessing network services?
- address spoofing
- MITM
- session hijacking
- DoS
9. Which requirement of secure communications is ensured by the implementation of MD5 or SHA hash generating algorithms?
- nonrepudiation
- authentication
- integrity
- confidentiality
10. If an asymmetric algorithm uses a public key to encrypt data, what is used to decrypt it?
- a digital certificate
- a different public key
- a private key
- DH
11. Refer to the exhibit. Which two ACLs would permit only the two LAN networks attached to R1 to access the network that connects to R2 G0/1 interface? (Choose two.)
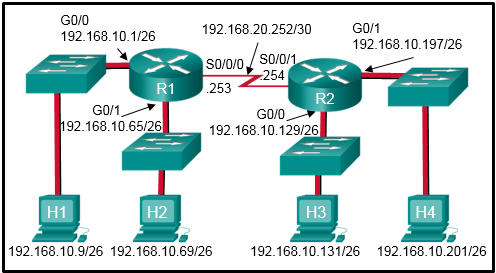
- access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.127
- access-list 2 permit host 192.168.10.9
access-list 2 permit host 192.168.10.69 - access-list 5 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.63
access-list 5 permit 192.168.10.64 0.0.0.63 - access-list 3 permit 192.168.10.128 0.0.0.63
- access-list 4 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
12. Which two packet filters could a network administrator use on an IPv4 extended ACL? (Choose two.)
- destination UDP port number
- computer type
- destination MAC address
- ICMP message type
- source TCP hello address
13. What type of ACL offers greater flexibility and control over network access?
- numbered standard
- named standard
- extended
- flexible
14. What is the quickest way to remove a single ACE from a named ACL?
- Use the no keyword and the sequence number of the ACE to be removed.
- Copy the ACL into a text editor, remove the ACE, then copy the ACL back into the router.
- Create a new ACL with a different number and apply the new ACL to the router interface.
- Use the no access-list command to remove the entire ACL, then recreate it without the ACE.
15. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring a standard IPv4 ACL. What is the effect after the command no access-list 10 is entered?
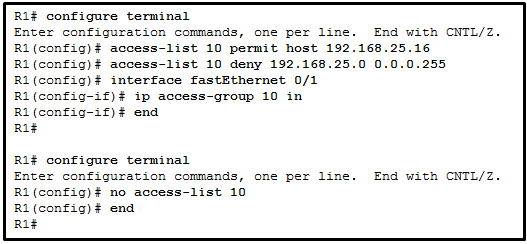
- ACL 10 is removed from both the running configuration and the interface Fa0/1.
- ACL 10 is removed from the running configuration.
- ACL 10 is disabled on Fa0/1.
- ACL 10 will be disabled and removed after R1 restarts.
16. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured ACL 9 as shown. Users on the 172.31.1.0 /24 network cannot forward traffic through router CiscoVille. What is the most likely cause of the traffic failure?
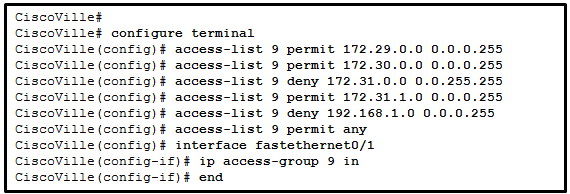
- The established keyword is not specified.
- The sequence of the ACEs is incorrect.
- The port number for the traffic has not been identified with the eq keyword.
- The permit statement specifies an incorrect wildcard mask.
17. A network administrator needs to configure a standard ACL so that only the workstation of the administrator with the IP address 192.168.15.23 can access the virtual terminal of the main router. Which two configuration commands can achieve the task? (Choose two.)
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 0.0.0.0
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 0.0.0.255
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 255.255.255.255
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit host 192.168.15.23
- Router1(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.15.23 255.255.255.0
18. Refer to the exhibit. Which command would be used in a standard ACL to allow only devices on the network attached to R2 G0/0 interface to access the networks attached to R1?
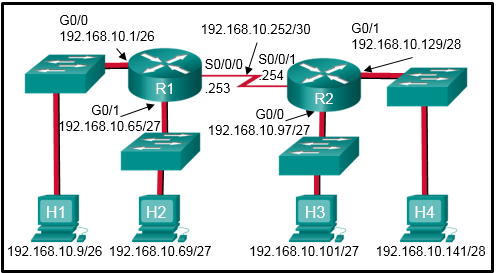
- access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.128 0.0.0.63
- access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
- access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.96 0.0.0.31
- access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.63
19. A network administrator is writing a standard ACL that will deny any traffic from the 172.16.0.0/16 network, but permit all other traffic. Which two commands should be used? (Choose two.)
- Router(config)# access-list 95 deny 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0
- Router(config)# access-list 95 permit any
- Router(config)# access-list 95 host 172.16.0.0
- Router(config)# access-list 95 deny 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255
- Router(config)# access-list 95 172.16.0.0 255.255.255.255
- Router(config)# access-list 95 deny any
20. Refer to the exhibit. An ACL was configured on R1 with the intention of denying traffic from subnet 172.16.4.0/24 into subnet 172.16.3.0/24. All other traffic into subnet 172.16.3.0/24 should be permitted. This standard ACL was then applied outbound on interface Fa0/0. Which conclusion can be drawn from this configuration?
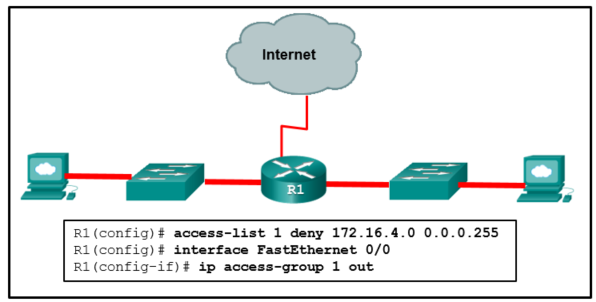
- The ACL should be applied outbound on all interfaces of R1.
- The ACL should be applied to the FastEthernet 0/0 interface of R1 inbound to accomplish the requirements.
- All traffic will be blocked, not just traffic from the 172.16.4.0/24 subnet.
- Only traffic from the 172.16.4.0/24 subnet is blocked, and all other traffic is allowed.
- An extended ACL must be used in this situation.
21. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to add an ACE to the TRAFFIC-CONTROL ACL that will deny IP traffic from the subnet 172.23.16.0/20. Which ACE will meet this requirement?
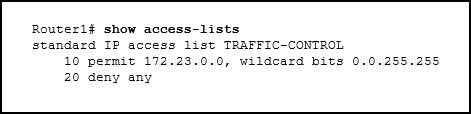
- 30 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.15.255
- 15 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.15.255
- 5 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.15.255
- 5 deny 172.23.16.0 0.0.255.255
22. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator configures an ACL on the router. Which statement describes the result of the configuration?
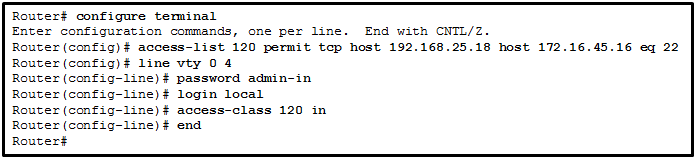
- An SSH connection is allowed from a workstation with IP 172.16.45.16 to a device with IP 192.168.25.18.
- An SSH connection is allowed from a workstation with IP 192.168.25.18 to a device with IP 172.16.45.16.
- A Telnet connection is allowed from a workstation with IP 192.168.25.18 to a device with IP 172.16.45.16.
- A Telnet connection is allowed from a workstation with IP 172.16.45.16 to a device with IP 192.168.25.18.
23. Refer to the exhibit. What can be determined from this output?
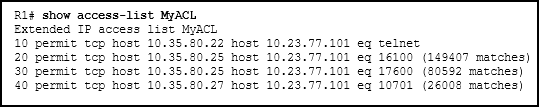
- The ACL is missing the deny ip any any ACE.
- The ACL is only monitoring traffic destined for 10.23.77.101 from three specific hosts.
- Because there are no matches for line 10, the ACL is not working.
- The router has not had any Telnet packets from 10.35.80.22 that are destined for 10.23.77.101.
24. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator wants to permit only host 192.168.1.1 /24 to be able to access the server 192.168.2.1 /24. Which three commands will achieve this using best ACL placement practices? (Choose three.)
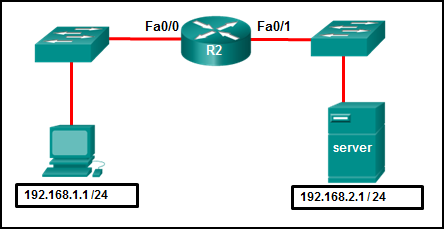
- R2(config)# interface fastethernet 0/1
- R2(config-if)# ip access-group 101 out
- R2(config)# access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0
- R2(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in
- R2(config)# access-list 101 permit ip any any
- R2(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
- R2(config)# access-list 101 permit ip host 192.168.1.1 host 192.168.2.1
25. Consider the following access list.
access-list 100 permit ip host 192.168.10.1 any
access-list 100 deny icmp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any echo
access-list 100 permit ip any any
access-list 100 deny icmp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any echo
access-list 100 permit ip any any
Which two actions are taken if the access list is placed inbound on a router Gigabit Ethernet port that has the IP address 192.168.10.254 assigned? (Choose two.)
- Only Layer 3 connections are allowed to be made from the router to any other network device.
- Devices on the 192.168.10.0/24 network are not allowed to reply to any ping requests.
- Devices on the 192.168.10.0/24 network can sucessfully ping devices on the 192.168.11.0 network.
- A Telnet or SSH session is allowed from any device on the 192.168.10.0 into the router with this access list assigned.
- Only the network device assigned the IP address 192.168.10.1 is allowed to access the router.
26. Refer to the exhibit. The named ACL “Managers” already exists on the router. What will happen when the network administrator issues the commands that are shown in the exhibit?
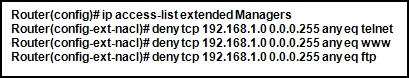
- The commands are added at the end of the existing Managers ACL.
- The commands overwrite the existing Managers ACL.
- The commands are added at the beginning of the existing Managers ACL.
- The network administrator receives an error that states that the ACL already exists.
27. In which TCP attack is the cybercriminal attempting to overwhelm a target host with half-open TCP connections?
- port scan attack
- SYN flood attack
- session hijacking attack
- reset attack
28. Which protocol is attacked when a cybercriminal provides an invalid gateway in order to create a man-in-the-middle attack?
- DHCP
- DNS
- ICMP
- HTTP or HTTPS
29. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator has configured a standard ACL on R1 and applied it to interface serial 0/0/0 in the outbound direction. What happens to traffic leaving interface serial 0/0/0 that does not match the configured ACL statements?
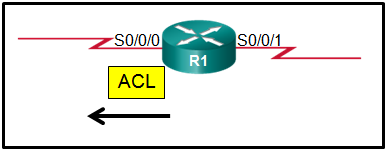
- The traffic is dropped.
- The source IP address is checked and, if a match is not found, traffic is routed out interface serial 0/0/1.
- The resulting action is determined by the destination IP address.
- The resulting action is determined by the destination IP address and port number.
30. Refer to the exhibit. The Gigabit interfaces on both routers have been configured with subinterface numbers that match the VLAN numbers connected to them. PCs on VLAN 10 should be able to print to the P1 printer on VLAN 12. PCs on VLAN 20 should print to the printers on VLAN 22. What interface and in what direction should you place a standard ACL that allows printing to P1 from data VLAN 10, but stops the PCs on VLAN 20 from using the P1 printer? (Choose two.)
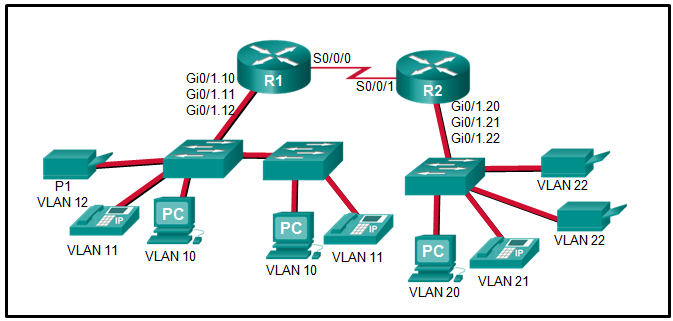
- inbound
- R2 S0/0/1
- R1 Gi0/1.12
- outbound
- R1 S0/0/0
- R2 Gi0/1.20
31. Which statement describes a characteristic of standard IPv4 ACLs?
- They are configured in the interface configuration mode.
- They can be configured to filter traffic based on both source IP addresses and source ports.
- They can be created with a number but not with a name.
- They filter traffic based on source IP addresses only.
32. What is considered a best practice when configuring ACLs on vty lines?
- Place identical restrictions on all vty lines.
- Remove the vty password since the ACL restricts access to trusted users.
- Apply the ip access-group command inbound.
- Use only extended access lists.
33.
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator first configured an extended ACL as shown by the output of the show access-lists command. The administrator then edited this access-list by issuing the commands below.

Refer to the exhibit. An administrator first configured an extended ACL as shown by the output of the show access-lists command. The administrator then edited this access-list by issuing the commands below.
Router(config)# ip access-list extended 101 Router(config-ext-nacl)# no 20 Router(config-ext-nacl)# 5 permit tcp any any eq 22 Router(config-ext-nacl)# 20 deny udp any any
Which two conclusions can be drawn from this new configuration? (Choose two.)
- TFTP packets will be permitted.
- Ping packets will be permitted.
- Telnet packets will be permitted.
- SSH packets will be permitted.
- All TCP and UDP packets will be denied.
34. Which set of access control entries would allow all users on the 192.168.10.0/24 network to access a web server that is located at 172.17.80.1, but would not allow them to use Telnet?
- access-list 103 deny tcp host 192.168.10.0 any eq 23
access-list 103 permit tcp host 192.168.10.1 eq 80 - access-list 103 permit tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 80
access-list 103 deny tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 23 - access-list 103 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 host 172.17.80.1
access-list 103 deny tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq telnet - access-list 103 permit tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 host 172.17.80.1 eq 80
access-list 103 deny tcp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 23
35. What is the term used to describe a mechanism that takes advantage of a vulnerability?
- mitigation
- exploit
- vulnerability
- threat
36. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator has an IP address of 192.168.11.10 and needs access to manage R1. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
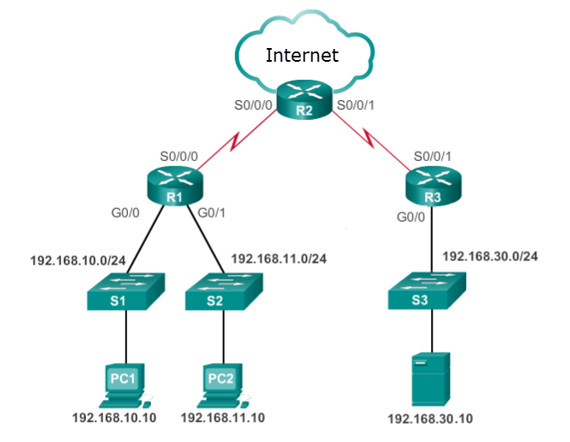
- extended ACL outbound on R2 WAN interface towards the internet
- standard ACL inbound on R1 vty lines
- extended ACLs inbound on R1 G0/0 and G0/1
- extended ACL outbound on R2 S0/0/1
37. A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the any configuration option or command?
- to add a text entry for documentation purposes
- to generate and send an informational message whenever the ACE is matched
- to identify any IP address
- to identify one specific IP address
38. Which statement accurately characterizes the evolution of threats to network security?
- Internet architects planned for network security from the beginning.
- Early Internet users often engaged in activities that would harm other users.
- Internal threats can cause even greater damage than external threats.
- Threats have become less sophisticated while the technical knowledge needed by an attacker has grown.
39. A user receives a phone call from a person who claims to represent IT services and then asks that user for confirmation of username and password for auditing purposes. Which security threat does this phone call represent?
- spam
- social engineering
- DDoS
- anonymous keylogging
40. In what way are zombies used in security attacks?
- They target specific individuals to gain corporate or personal information.
- They probe a group of machines for open ports to learn which services are running.
- They are maliciously formed code segments used to replace legitimate applications.
- They are infected machines that carry out a DDoS attack.
41. Which attack involves threat actors positioning themselves between a source and destination with the intent of transparently monitoring, capturing, and controlling the communication?
- man-in-the-middle attack
- SYN flood attack
- DoS attack
- ICMP attack
42. Which two keywords can be used in an access control list to replace a wildcard mask or address and wildcard mask pair? (Choose two.)
- host
- most
- gt
- some
- any
- all
43. Which statement describes a difference between the operation of inbound and outbound ACLs?
- Inbound ACLs are processed before the packets are routed while outbound ACLs are processed after the routing is completed.
- In contrast to outbound ALCs, inbound ACLs can be used to filter packets with multiple criteria.
- On a network interface, more than one inbound ACL can be configured but only one outbound ACL can be configured.
- Inbound ACLs can be used in both routers and switches but outbound ACLs can be used only on routers.
44. What effect would the Router1(config-ext-nacl)# permit tcp 172.16.4.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www command have when implemented inbound on the f0/0 interface?
- All TCP traffic is permitted, and all other traffic is denied.
- Traffic originating from 172.16.4.0/24 is permitted to all TCP port 80 destinations.
- All traffic from 172.16.4.0/24 is permitted anywhere on any port.
- The command is rejected by the router because it is incomplete.
45. Which ACE will permit a packet that originates from any network and is destined for a web server at 192.168.1.1?
- access-list 101 permit tcp any host 192.168.1.1 eq 80
- access-list 101 permit tcp host 192.168.1.1 eq 80 any
- access-list 101 permit tcp host 192.168.1.1 any eq 80
- access-list 101 permit tcp any eq 80 host 192.168.1.1
46. Refer to the exhibit. A new network policy requires an ACL denying FTP and Telnet access to a Corp file server from all interns. The address of the file server is 172.16.1.15 and all interns are assigned addresses in the 172.18.200.0/24 network. After implementing the ACL, no one in the Corp network can access any of the servers. What is the problem?
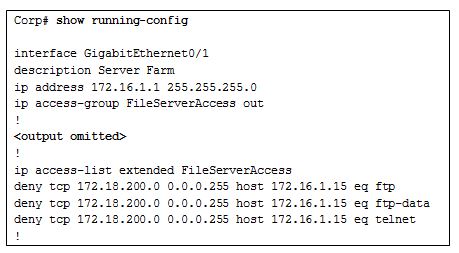
CCNA 3 v7 Modules 3 – 5: Network Security Exam Answers 46
- Inbound ACLs must be routed before they are processed.
- The ACL is implicitly denying access to all the servers.
- Named ACLs require the use of port numbers.
- The ACL is applied to the interface using the wrong direction.
47. A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the access-class 20 in configuration option or command?
- to secure administrative access to the router
- to remove an ACL from an interface
- to remove a configured ACL
- to apply a standard ACL to an interface
48. What is the term used to describe the same pre-shared key or secret key, known by both the sender and receiver to encrypt and decrypt data?
- symmetric encryption algorithm
- data integrity
- exploit
- risk
49. Refer to the exhibit. Internet privileges for an employee have been revoked because of abuse but the employee still needs access to company resources. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
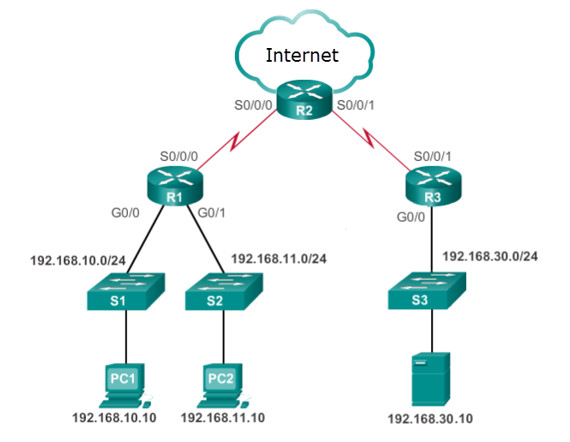
CCNA 3 v7 Modules 3 – 5: Network Security Exam Answers 49
- standard ACL inbound on R2 WAN interface connecting to the internet
- standard ACL outbound on R2 WAN interface towards the internet
- standard ACL inbound on R1 G0/0
- standard ACL outbound on R1 G0/0
50. Refer to the exhibit. The student on the H1 computer continues to launch an extended ping with expanded packets at the student on the H2 computer. The school network administrator wants to stop this behavior, but still allow both students access to web-based computer assignments. What would be the best plan for the network administrator?
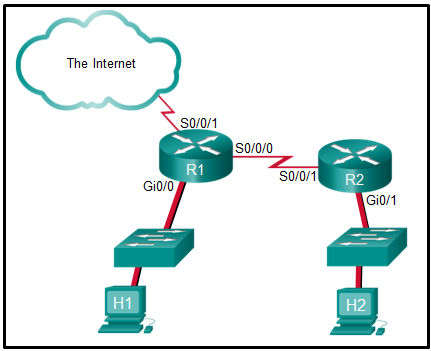
CCNA 3 v7 Modules 3 – 5: Network Security Exam Answers 42
- Apply an inbound standard ACL on R1 Gi0/0.
- Apply an inbound extended ACL on R2 Gi0/1.
- Apply an outbound extended ACL on R1 S0/0/1.
- Apply an inbound extended ACL on R1 Gi0/0.
- Apply an outbound standard ACL on R2 S0/0/1.
51. A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the ‘ip access-group 101 in’ configuration option or command?
- to apply an extended ACL to an interface
- to secure management traffic into the router
- to secure administrative access to the router
- to display all restricted traffic
52. In which type of attack is falsified information used to redirect users to malicious Internet sites?
- DNS amplification and reflection
- ARP cache poisoning
- DNS cache poisoning
- domain generation
53. What is a feature of an IPS?
- It can stop malicious packets.
- It is deployed in offline mode.
- It has no impact on latency.
- It is primarily focused on identifying possible incidents.
54. What is the term used to describe a potential danger to a company’s assets, data, or network functionality?
- vulnerability
- threat
- asset
- exploit
55. Refer to the exhibit. Network 192.168.30.0/24 contains all of the company servers. Policy dictates that traffic from the servers to both networks 192.168.10.0 and 192.168.11.0 be limited to replies for original requests. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
- standard ACL inbound on R1 vty lines
- extended ACLs inbound on R1 G0/0 and G0/1
- extended ACL inbound on R3 G0/0
- extended ACL inbound on R3 S0/0/1
56. What does the CLI prompt change to after entering the command ip access-list standard aaa from global configuration mode?
- Router(config-line)#
- Router(config-std-nacl)#
- Router(config)#
- Router(config-router)#
- Router(config-if)#
57. Refer to the exhibit. Many employees are wasting company time accessing social media on their work computers. The company wants to stop this access. What is the best ACL type and placement to use in this situation?
- extended ACL outbound on R2 WAN interface towards the internet
- standard ACL outbound on R2 WAN interface towards the internet
- standard ACL outbound on R2 S0/0/0
- extended ACLs inbound on R1 G0/0 and G0/1
58. A technician is tasked with using ACLs to secure a router. When would the technician use the 40 deny host 192.168.23.8 configuration option or command?
- to remove all ACLs from the router
- to create an entry in a numbered ACL
- to apply an ACL to all router interfaces
- to secure administrative access to the router
59. What is the best description of Trojan horse malware?
- It is malware that can only be distributed over the Internet.
- It appears as useful software but hides malicious code.
- It is software that causes annoying but not fatal computer problems.
- It is the most easily detected form of malware.
60. What wild card mask will match networks 172.16.0.0 through 172.19.0.0?
- 0.0.3.255
- 0.252.255.255
- 0.3.255.255
- 0.0.255.255