- ARP spoofing
- DHCP starvation
- IP address spoofing
- MAC address flooding
2. What mitigation plan is best for thwarting a DoS attack that is creating a MAC address table overflow?
- Disable DTP.
- Disable STP.
- Enable port security.
- Place unused ports in an unused VLAN.
3. Which three Cisco products focus on endpoint security solutions? (Choose three.)
- IPS Sensor Appliance
- Web Security Appliance
- Email Security Appliance
- SSL/IPsec VPN Appliance
- Adaptive Security Appliance
- NAC Appliance
4. True or False?
In the 802.1X standard, the client attempting to access the network is referred to as the supplicant.
In the 802.1X standard, the client attempting to access the network is referred to as the supplicant.
- true
- false
5. Which authentication method stores usernames and passwords in the router and is ideal for small networks?
- server-based AAA over TACACS+
- local AAA over RADIUS
- server-based AAA
- local AAA over TACACS+
- local AAA
- server-based AAA over RADIUS
6. What represents a best practice concerning discovery protocols such as CDP and LLDP on network devices?
- Enable CDP on edge devices, and enable LLDP on interior devices.
- Use the open standard LLDP rather than CDP.
- Use the default router settings for CDP and LLDP.
- Disable both protocols on all interfaces where they are not required.
7. Which protocol should be used to mitigate the vulnerability of using Telnet to remotely manage network devices?
- SNMP
- TFTP
- SSH
- SCP
8. Which statement describes the behavior of a switch when the MAC address table is full?
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports on the switch.
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports across multiple switches.
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports within the local VLAN.
- It treats frames as unknown unicast and floods all incoming frames to all ports within the collision domain.
9. What device is considered a supplicant during the 802.1X authentication process?
- the router that is serving as the default gateway
- the authentication server that is performing client authentication
- the client that is requesting authentication
- the switch that is controlling network access
10. Refer to the exhibit. Port Fa0/2 has already been configured appropriately. The IP phone and PC work properly. Which switch configuration would be most appropriate for port Fa0/2 if the network administrator has the following goals?
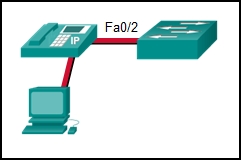
No one is allowed to disconnect the IP phone or the PC and connect some other wired device.
If a different device is connected, port Fa0/2 is shut down.
The switch should automatically detect the MAC address of the IP phone and the PC and add those addresses to the running configuration.
If a different device is connected, port Fa0/2 is shut down.
The switch should automatically detect the MAC address of the IP phone and the PC and add those addresses to the running configuration.
- SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky - SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 2
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security violation restrict - SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 2 - SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 2
SWA(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
11. Refer to the exhibit. Port security has been configured on the Fa 0/12 interface of switch S1. What action will occur when PC1 is attached to switch S1 with the applied configuration?
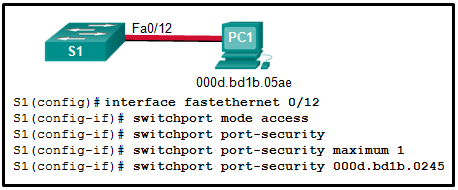
- Frames from PC1 will be forwarded since the switchport port-security violation command is missing.
- Frames from PC1 will be forwarded to its destination, and a log entry will be created.
- Frames from PC1 will be forwarded to its destination, but a log entry will not be created.
- Frames from PC1 will cause the interface to shut down immediately, and a log entry will be made.
- Frames from PC1 will be dropped, and there will be no log of the violation.
- Frames from PC1 will be dropped, and a log message will be created.
12. Which type of VLAN-hopping attack may be prevented by designating an unused VLAN as the native VLAN?
- DHCP spoofing
- DHCP starvation
- VLAN double-tagging
- DTP spoofing
13. A network administrator is configuring DAI on a switch with the command ip arp inspection validate src-mac. What is the purpose of this configuration command?
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the user-configured ARP ACLs.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the MAC address table.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the sender MAC address in the ARP body.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the target MAC address in the ARP body.
14. Which two commands can be used to enable BPDU guard on a switch? (Choose two.)
- S1(config)# spanning-tree bpduguard default
- S1(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast bpduguard
- S1(config)# spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default
- S1(config-if)# enable spanning-tree bpduguard
- S1(config-if)# spanning-tree bpduguard enable
15. As part of the new security policy, all switches on the network are configured to automatically learn MAC addresses for each port. All running configurations are saved at the start and close of every business day. A severe thunderstorm causes an extended power outage several hours after the close of business. When the switches are brought back online, the dynamically learned MAC addresses are retained. Which port security configuration enabled this?
- auto secure MAC addresses
- dynamic secure MAC addresses
- static secure MAC addresses
- sticky secure MAC addresses
16. Which type of management frame may regularly be broadcast by an AP?
- authentication
- probe request
- probe response
- beacon
17. What are the two methods that are used by a wireless NIC to discover an AP? (Choose two.)
- delivering a broadcast frame
- receiving a broadcast beacon frame
- initiating a three-way handshake
- sending an ARP request
- transmitting a probe request
18. A technician is configuring the channel on a wireless router to either 1, 6, or 11. What is the purpose of adjusting the channel?
- to enable different 802.11 standards
- to avoid interference from nearby wireless devices
- to disable broadcasting of the SSID
- to provide stronger security modes
19. While attending a conference, participants are using laptops for network connectivity. When a guest speaker attempts to connect to the network, the laptop fails to display any available wireless networks. The access point must be operating in which mode?
- mixed
- passive
- active
- open
20. A network administrator is required to upgrade wireless access to end users in a building. To provide data rates up to 1.3 Gb/s and still be backward compatible with older devices, which wireless standard should be implemented?
- 802.11n
- 802.11ac
- 802.11g
- 802.11b
21. A technician is about to install and configure a wireless network at a small branch office. What is the first security measure the technician should apply immediately upon powering up the wireless router?
- Enable MAC address filtering on the wireless router.
- Configure encryption on the wireless router and the connected wireless devices.
- Change the default user-name and password of the wireless router.
- Disable the wireless network SSID broadcast.
22. On a Cisco 3504 WLC dashboard, which option provides access to the full menu of features?
- Access Points
- Network Summary
- Advanced
- Rogues
23. Which step is required before creating a new WLAN on a Cisco 3500 series WLC?
- Create a new SSID.
- Build or have an SNMP server available.
- Build or have a RADIUS server available.
- Create a new VLAN interface.
24. A network engineer is troubleshooting a newly deployed wireless network that is using the latest 802.11 standards. When users access high bandwidth services such as streaming video, the wireless network performance is poor. To improve performance the network engineer decides to configure a 5 Ghz frequency band SSID and train users to use that SSID for streaming media services. Why might this solution improve the wireless network performance for that type of service?
- Requiring the users to switch to the 5 GHz band for streaming media is inconvenient and will result in fewer users accessing these services.
- The 5 GHz band has more channels and is less crowded than the 2.4 GHz band, which makes it more suited to streaming multimedia.
- The 5 GHz band has a greater range and is therefore likely to be interference-free.
- The only users that can switch to the 5 GHz band will be those with the latest wireless NICs, which will reduce usage.
25. A network administrator is configuring a RADIUS server connection on a Cisco 3500 series WLC. The configuration requires a shared secret password. What is the purpose for the shared secret password?
- It is used by the RADIUS server to authenticate WLAN users.
- It is used to authenticate and encrypt user data on the WLAN.
- It is used to encrypt the messages between the WLC and the RADIUS server.
- It allows users to authenticate and access the WLAN.
26. Which three parameters would need to be changed if best practices are being implemented for a home wireless AP? (Choose three.)
- wireless client operating system password
- antenna frequency
- wireless network password
- wireless beacon time
- AP password
- SSID
27. Which access control component, implementation, or protocol is based upon usernames and passwords?
- 802.1X
- accounting
- authentication
- authorization
28. Which type of wireless network is based on the 802.11 standard and a 2.4-GHz or 5-GHz radio frequency?
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless wide-area network
- wireless local-area network
- wireless personal-area network
29. Which two Cisco solutions help prevent DHCP starvation attacks? (Choose two.)
- DHCP Snooping
- IP Source Guard
- Dynamic ARP Inspection
- Port Security
- Web Security Appliance
30. What are three techniques for mitigating VLAN attacks? (Choose three.)
- Enable trunking manually.
- Disable DTP.
- Enable Source Guard.
- Set the native VLAN to an unused VLAN.
- Use private VLANs.
- Enable BPDU guard.
31. Refer to the exhibit. What can be determined about port security from the information that is shown?
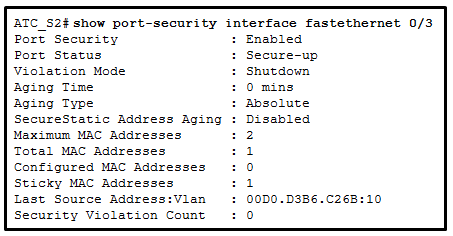
- The port has the maximum number of MAC addresses that is supported by a Layer 2 switch port which is configured for port security.
- The port has been shut down.
- The port violation mode is the default for any port that has port security enabled.
- The port has two attached devices.
32. A network administrator of a college is configuring the WLAN user authentication process. Wireless users are required to enter username and password credentials that will be verified by a server. Which server would provide such service?
- AAA
- NAT
- RADIUS
- SNMP
33. A technician is troubleshooting a slow WLAN that consists of 802.11b and 802.11g devices . A new 802.11n/ac dual-band router has been deployed on the network to replace the old 802.11g router. What can the technician do to address the slow wireless speed?
- Split the wireless traffic between the 802.11n 2.4 GHz band and the 5 GHz band.
- Update the firmware on the new router.
- Configure devices to use a different channel.
- Change the SSID.
34. The company handbook states that employees cannot have microwave ovens in their offices. Instead, all employees must use the microwave ovens located in the employee cafeteria. What wireless security risk is the company trying to avoid?
- improperly configured devices
- rogue access points
- accidental interference
- interception of data
35. What is the function provided by CAPWAP protocol in a corporate wireless network?
- CAPWAP creates a tunnel on Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) ports in order to allow a WLC to configure an autonomous access point.
- CAPWAP provides the encapsulation and forwarding of wireless user traffic between an access point and a wireless LAN controller.
- CAPWAP provides connectivity between an access point using IPv6 addressing and a wireless client using IPv4 addressing.
- CAPWAP provides the encryption of wireless user traffic between an access point and a wireless client.
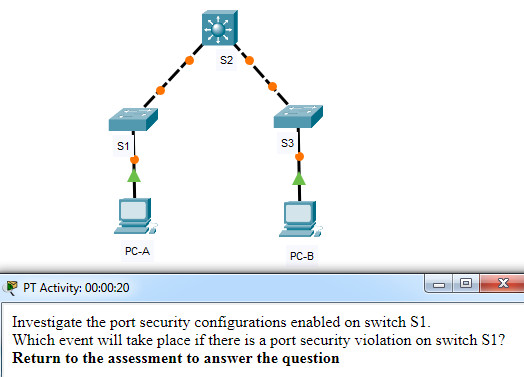
36. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Modules 10 – 13: L2 Security and WLANs Exam Answers
Which event will take place if there is a port security violation on switch S1 interface Fa0/1?
- A syslog message is logged.
- The interface will go into error-disabled state.
- Packets with unknown source addresses will be dropped.
- A notification is sent.
37. Match each functional component of AAA with its description. (Not all options are used.)
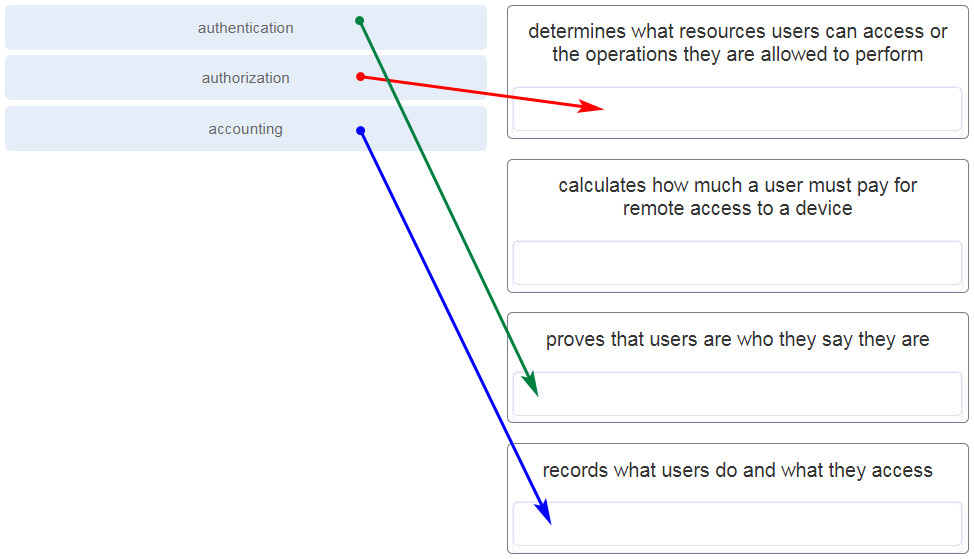

38. What are two protocols that are used by AAA to authenticate users against a central database of usernames and password? (Choose two.)
- SSH
- HTTPS
- TACACS+
- RADIUS
- CHAP
- NTP
39. What is the result of a DHCP starvation attack?
- The attacker provides incorrect DNS and default gateway information to clients.
- The IP addresses assigned to legitimate clients are hijacked.
- Clients receive IP address assignments from a rogue DHCP server.
- Legitimate clients are unable to lease IP addresses.
40. Which feature or configuration on a switch makes it vulnerable to VLAN double-tagging attacks?
- the limited size of content-addressable memory space
- the automatic trunking port feature enabled for all ports by default
- the native VLAN of the trunking port being the same as a user VLAN
- mixed duplex mode enabled for all ports by default
41. Which component of AAA allows an administrator to track individuals who access network resources and any changes that are made to those resources?
- authentication
- accounting
- accessibility
- authorization
42. Refer to the exhibit. PC1 and PC2 should be able to obtain IP address assignments from the DHCP server. How many ports among switches should be assigned as trusted ports as part of the DHCP snooping configuration?
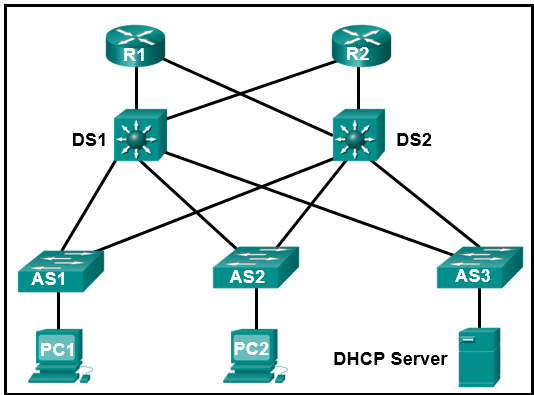
- 1
- 3
- 5
- 7
43. An IT security specialist enables port security on a switch port of a Cisco switch. What is the default violation mode in use until the switch port is configured to use a different violation mode?
- shutdown
- disabled
- restrict
- protect
44. A laptop cannot connect to a wireless access point. Which two troubleshooting steps should be taken first? (Choose two.)
- Ensure that the correct network media is selected.
- Ensure that the laptop antenna is attached.
- Ensure that the wireless NIC is enabled.
- Ensure that the wireless SSID is chosen.
- Ensure that the NIC is configured for the proper frequency.
45. What is an advantage of SSID cloaking?
- Clients will have to manually identify the SSID to connect to the network.
- It is the best way to secure a wireless network.
- SSIDs are very difficult to discover because APs do not broadcast them.
- It provides free Internet access in public locations where knowing the SSID is of no concern.
46. What is a wireless security mode that requires a RADIUS server to authenticate wireless users?
- personal
- shared key
- enterprise
- WEP
47. A company has recently implemented an 802.11n wireless network. Some users are complaining that the wireless network is too slow. Which solution is the best method to enhance the performance of the wireless network?
- Disable DHCP on the access point and assign static addresses to the wireless clients.
- Upgrade the firmware on the wireless access point.
- Split the traffic between the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.
- Replace the wireless NICs on the computers that are experiencing slow connections.
48. Which protocol can be used to monitor the network?
- DHCP
- SNMP
- RADIUS
- AAA
49. A network administrator deploys a wireless router in a small law firm. Employee laptops join the WLAN and receive IP addresses in the 10.0.10.0/24 network. Which service is used on the wireless router to allow the employee laptops to access the internet?
- DHCP
- RADIUS
- DNS
- NAT
50. Which service can be used on a wireless router to prioritize network traffic among different types of applications so that voice and video data are prioritized over email and web data?
- QoS
- DNS
- DHCP
- NAT
51. Which access control component, implementation, or protocol is based on device roles of supplicant, authenticator, and authentication server?
- accounting
- authentication
- authorization
- 802.1X
52. Which type of wireless network is suitable for national and global communications?
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless local-area network
- wireless personal-area network
- wireless wide-area network
53. Which feature on a switch makes it vulnerable to VLAN hopping attacks?
- the mixed duplex mode enabled for all ports by default
- the limited size of content-addressable memory space
- mixed port bandwidth support enabled for all ports by default
- the automatic trunking port feature enabled for all ports by default
54. Which component of AAA is used to determine which resources a user can access and which operations the user is allowed to perform?
- accounting
- authentication
- auditing
- authorization
55. Refer to the exhibit. The Fa0/2 interface on switch S1 has been configured with the switchport port-security mac-address 0023.189d.6456 command and a workstation has been connected. What could be the reason that the Fa0/2 interface is shutdown?
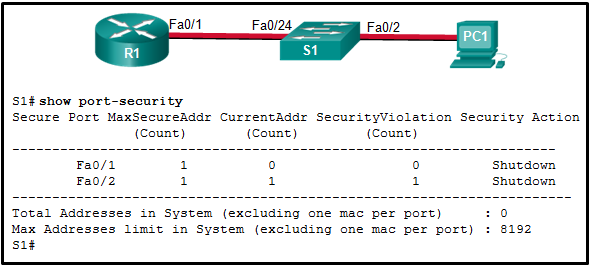
CCNA 2 v7 Modules 10 – 13: L2 Security and WLANs Exam Answers 55
- The Fa0/24 interface of S1 is configured with the same MAC address as the Fa0/2 interface.
- The connection between S1 and PC1 is via a crossover cable.
- S1 has been configured with a
switchport port-security agingcommand. - The MAC address of PC1 that connects to the Fa0/2 interface is not the configured MAC address.
56. A network administrator enters the following commands on the switch SW1.
SW1(config)# interface range fa0/5 - 10 SW1(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping limit rate 6
What is the effect after these commands are entered?
- If any of the FastEthernet ports 5 through 10 receive more than 6 DHCP messages per second, the port will be shut down.
- FastEthernet ports 5 through 10 can receive up to 6 DHCP messages per second of any type.
- If any of the FastEthernet ports 5 through 10 receive more than 6 DHCP messages per second, the port will continue to operate and an error message will be sent to the network administrator.
- FastEthernet ports 5 through 10 can receive up to 6 DHCP discovery messages per second.
57. A network administrator is configuring port security on a Cisco switch. The company security policy specifies that when a violation occurs, packets with unknown source addresses should be dropped and no notification should be sent. Which violation mode should be configured on the interfaces?
- off
- restrict
- protect
- shutdown
58. A network administrator is working to improve WLAN performance on a dual-band wireless router. What is a simple way to achieve a split-the-traffic result?
- Add a Wi-Fi range extender to the WLAN and set the AP and the range extender to serve different bands.
- Check and keep the firmware of the wireless router updated.
- Make sure that different SSIDs are used for the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
- Require all wireless devices to use the 802.11n standard.
59. Which access control component, implementation, or protocol controls what users can do on the network?
- accounting
- 802.1X
- authorization
- authentication
60. Which type of wireless network is suitable for providing wireless access to a city or district?
- wireless wide-area network
- wireless personal-area network
- wireless local-area network
- wireless metropolitan-area network
61. On a Cisco 3504 WLC Summary page ( Advanced > Summary ), which tab allows a network administrator to access and configure a WLAN for a specific security option such as WPA2?
- MANAGEMENT
- WIRELESS
- WLANs
- SECURITY
62. What type of wireless antenna is best suited for providing coverage in large open spaces, such as hallways or large conference rooms?
- Yagi
- omnidirectional
- dish
- directional
64. What security benefit is gained from enabling BPDU guard on PortFast enabled interfaces?
- preventing buffer overflow attacks
- preventing rogue switches from being added to the network
- protecting against Layer 2 loops
- enforcing the placement of root bridges
65. Which access control component, implementation, or protocol logs EXEC and configuration commands configured by a user?
- authentication
- authorization
- 802.1X
- accounting
66. Which type of wireless network uses transmitters to provide coverage over an extensive geographic area?
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless local-area network
- wireless personal-area network
- wireless wide-area network
67. Which access control component, implementation, or protocol controls who is permitted to access a network?
- authorization
- 802.1X
- accounting
- authentication
68. What two IEEE 802.11 wireless standards operate only in the 5 GHz range? (Choose two.)
- 802.11g
- 802.11ad
- 802.11ac
- 802.11a
- 802.11n
- 802.11b
69. Which type of wireless network uses low powered transmitters for a short-range network, usually 20 to 30 ft. (6 to 9 meters)?
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless personal-area network
- wireless local-area network
- wireless wide-area network
70. A network administrator is configuring DAI on a switch with the command ip arp inspection validate src-mac. What is the purpose of this configuration command?
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the user-configured ARP ACLs.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the MAC address table.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the target MAC address in the ARP body.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the sender MAC address in the ARP body.
71. Which wireless network topology would be used by network engineers to provide a wireless network for an entire college building?
- ad hoc
- hotspot
- infrastructure
- mixed mode
72. Which type of wireless network uses transmitters to provide wireless service over a large urban region?
- wireless wide-area network
- wireless personal-area network
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless local-area network.
73. Which type of wireless network is suitable for use in a home or office?
74. Which access control component, implementation, or protocol indicates success or failure of a client-requested service with a PASS or FAIL message?
- accounting
- authentication
- 802.1X
- authorization
75. Which type of wireless network often makes use of devices mounted on buildings?
- wireless local-area network
- wireless metropolitan-area network
- wireless personal-area network
- wireless wide-area network
76. A network administrator is configuring DAI on a switch with the command ip arp inspection validate src-mac . What is the purpose of this configuration command?
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the user-configured ARP ACLs.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the MAC address table.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the sender MAC address in the ARP body.
- It checks the source MAC address in the Ethernet header against the target MAC address in the ARP body.