CCNAv7: Switching, Routing, and Wireless Essentials v7.0 (SRWE)
Final PTSA Part 2
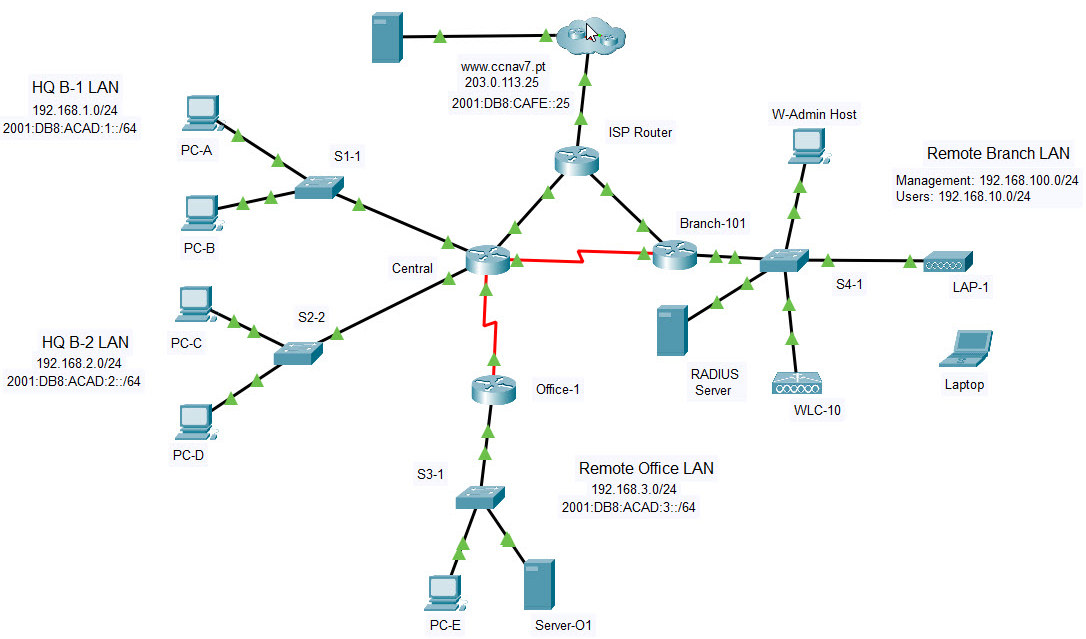
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | Address and Prefix |
|---|---|---|
| Central | G0/0/0 | 192.168.1.1/24 |
| 2001:db8:acad:1::1/64 | ||
| fe80::1 | ||
| G0/0/1 | 192.168.2.1/24 | |
| 2001:db8:acad:2::1/64 | ||
| fe80::1 | ||
| G0/0/2 | 10.1.0.1/30 | |
| 2001:db8:acad:a::1/64 | ||
| fe80::2 | ||
| S0/1/0 | 10.2.0.1/30 | |
| 2001:db8:acad:b::1/64 | ||
| fe80::2 | ||
| S0/1/1 | 10.4.0.1/30 | |
| 2001:db8:acad:d::1/64 | ||
| Office-1 | S0/1/1 | 10.4.0.2/30 |
| 2001:db8:acad:d::2/64 | ||
| fe80::2 | ||
| G0/0/0 | 192.168.3.1/24 | |
| 2001:db8:acad:3::1/64 | ||
| fe80::1 | ||
| Branch-101 | G0/0/0.10 | 192.168.10.1/24 |
| G0/0/0.100 | 192.168.100.1/24 | |
| G0/0/0.172 | 172.16.1.1/24 | |
| G0/0/1 | DHCP | |
| 2001:db8:acad:c::2/64 | ||
| S0/1/0 | 10.2.0.2/30 | |
| 2001:db8:acad:b::2/64 | ||
| ISP Router | G0/0/0 | 10.1.0.2/24 |
| 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::2/64 | ||
| G0/0/1 | 10.3.0.1/24 | |
| 2001:DB8:ACAD:C::1/64 | ||
| WLC-10 | management | 192.168.100.254 |
| WLAN 10 | 192.168.10.254/24 | |
| Server-01 | NIC | 192.168.3.122 |
| 2001:db8:acad:3::122 | ||
| Internet Server | NIC | 203.0.113.25 |
| 2001:db8:acad:cafe:25 | ||
| DNS Server | NIC | 198.51.100.163 |
| 2001:DB8:face::163 | ||
| Management Host | NIC | 192.168.100.23 |
| Wireless Host | NIC | DHCP |
| RADIUS server | NIC | 172.16.1.100/24 |
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.1.10/24 |
| 2001:db8:acad:1::10/64 | ||
| PC-B | NIC | 192.168.1.11/24 |
| 2001:db8:acad:1::11/64 | ||
| PC-C | NIC | 192.168.2.20/24 |
| 2001:db8:acad:2::20/64 | ||
| PC-D | NIC | 192.168.2.11/24 |
| 2001:db8:acad:2::21/64 | ||
| PC-E | NIC | 192.168.3.30/24 |
| 2001:db8:acad:3::30/64 |
Objectives
In this assessment, you will configure the following:
- Floating static and default routes in IPV4 and IPV6.
- Host routes in IPV4 and IPV6.
- DHCP pools and scopes.
- Switch security including port security.
- Enhanced LAN security with DHCP snooping, dynamic ARP inspection, PortFast, and BPDU guard.
- Wireless LAN Controller-based wireless LAN with enterprise authentication.
Background / Scenario
Netacad PLC is reworking their network. You have been asked to prototype the network in Packet Tracer for evaluation by senior network staff.
Instructions
Part 1: Configure Switch Security
In this part of the assessment you will configure switch S1-1 with switch security features. Switch ports FastEthernet0/1 to FastEthernet0/5 are the active switch ports. Port GigabitEthernet0/1 is a dedicated link to router Central. All other ports should be secured.
Step 1: Configure VLANs
a. Configure VLAN 10 with name users.
b. Configure VLAN 999 with the name unused.
Step 2: Configure active switch ports.
On the active switch ports configure the following:
a. Configure the ports FastEthernet 01 through 05 and port GigabitEthernet 0/1 as static access ports in VLAN 10.
b. Activate port security on the ports.
- Configure the ports to accept a maximum of 4 MAC addresses.
- If a violation occurs, configure the port to drop frames from the unauthorized MAC address, log it, and send an alert.
- MAC addresses should be present in the MAC address table for a maximum of 10 minutes before they are removed.
- Ports should add the learned MAC addresses to the running configuration.
- Configure the MAC address of PC-A as a static address on port FastEthernet0/1.
c. Protect against DHCP snooping.
- Activate DHCP snooping globally.
- Activate DHCP snooping for the two VLANs that you configured.
- Configure the ports to limit the rate to 5 DHCP packets per second.
- Configure the port that links to the router as trusted.
d. Guard against ARP attacks by implementing DAI.
- Activate DA globally.
- Activate Dal on the two VLANs.
- Configure the port that links to the router as trusted.
e. Secure STP by configuring PortFast and BPDUGuard
f. Mitigate STP attacks by configuring BPDUguard and PortFast on the active ports.
Step 3: Secure unused switch ports.
a. Move all unused switch ports to VLAN 999.
b. Configure all unused switch ports as static access ports.
C. Deactivate all unused switch ports.
Part 2: Configure Addressing and DHCP
You will configure DHCP and interface addressing on Branch-101 to prepare for implementing the wireless LAN controller network.
Step 1: Configure and address a subinterface for the WLAN user network.
a. Configure subinterface 10 on the router interface that is connected to the switch S4-1.
b. The router should provide router-on-a-stick routing to VLAN 10.
C. Configure the subinterface with the address from the Addressing Table.
Step 2: Configure a DHCP pool for WLAN user network.
a. Exclude the router interface address and the management address of the WLC.
b. Configure a DHCP pool that will be used by hosts that are connecting to the WLAN.
- Name the pool WLAN-hosts.
- Configure the pool to use addresses in the 192.168.10.0/24 network.
- The pool should also provide the default gateway and DNS server addresses.
Step 3: Configure an interface as a DHCP client.
On ERROR: VARIABLE NOT FOUND [[Cld_router-names]], configure the interface that is connected to the cloud to receive its address over DHCP.
Part 3: Configure Static Routes
In this part of the assessment you will configure static, default, floating static, and host routes in both IPv4 andl Pv6. You will configure the Central and Branch-101 routers. Netacad PLC has decided that it wants to use static routing between all its networks. In addition, the company wants to use the Ethernet links between routers for most data traffic and reserve serial link between Central and Branch-101 for backup purposes in case one of the Ethernet links becomes unavailable. You will be configuring floating static and default routes.
Step 1: Configure static routes on Central.
a. Configure IPv4 default routes to the cloud using the Ethernet link as the preferred link and the serial link as the backup. Use an administrative distance of 10 for the backup route. These routes should be directly connected. Note: Ethernet interfaces will give a warning when configured without a next-hop address. In this configuration, the interface is point-to point, so the warning can be ignored.
b. Configure IPv6 default routes to the cloud. Use the Ethernet link as the primary route, and the serial link as backup. Use an administrative distance of 10 for the backup route. These routes should specify the next hop interface address.
c. Configure IPv4 static routes to the Remote Office LAN WLAN user network following the same guidelines as above for type of route and administrative distance.
d. Configure IPv4 and IPv6 host routes on Central to the Server-01 on the Remote Office LAN. Create a directly connected route for IPv4 and a next-hop route for IPv6.
Step 2: Configure static routes on Branch-101.
Branch-101 must also be configured with static routes to the other three networks in the Netacad PLC network. It will require floating static and default routes in IPv4 and IPv6 following the same guidelines as were used for the Central static routes.
- IPv6 routes use next-hop address arguments.
- IPv4 routes use exit interface arguments.
- All routes should prefer the Ethernet links over the serial link.
- Backup floating routes use an administrative distance of 10.
a. Configure IPv4 default routes to the cloud using the Ethernet link as the preferred link and the serial link as the backup.
b. Configure IPv6 default routes to the cloud. Use the Ethernet link as the primary route, and the serial link as backup. Use an administrative distance of 10 for the backup route. These routes should specify the next hop interface address.
Part 4: Configure a Wireless LAN using a Wireless LAN Controller
In this part of the assessment, you will configure the wireless LAN controller to provide access wireless access to the network. Username and password are the default admin/admin.
Step 1: Configure a VLAN interface.
a. Create a new interface and name it WLAN 10. The interface should use VLAN 10.
b. Use the information in the addressing table to configure the addressing settings for the interface. The interface will be using a DHCP pool that will be assign addresses on the network configured on the subinterface assigned to VLAN 10 on router Branch-101
Step 2: Configure a RADIUS server.
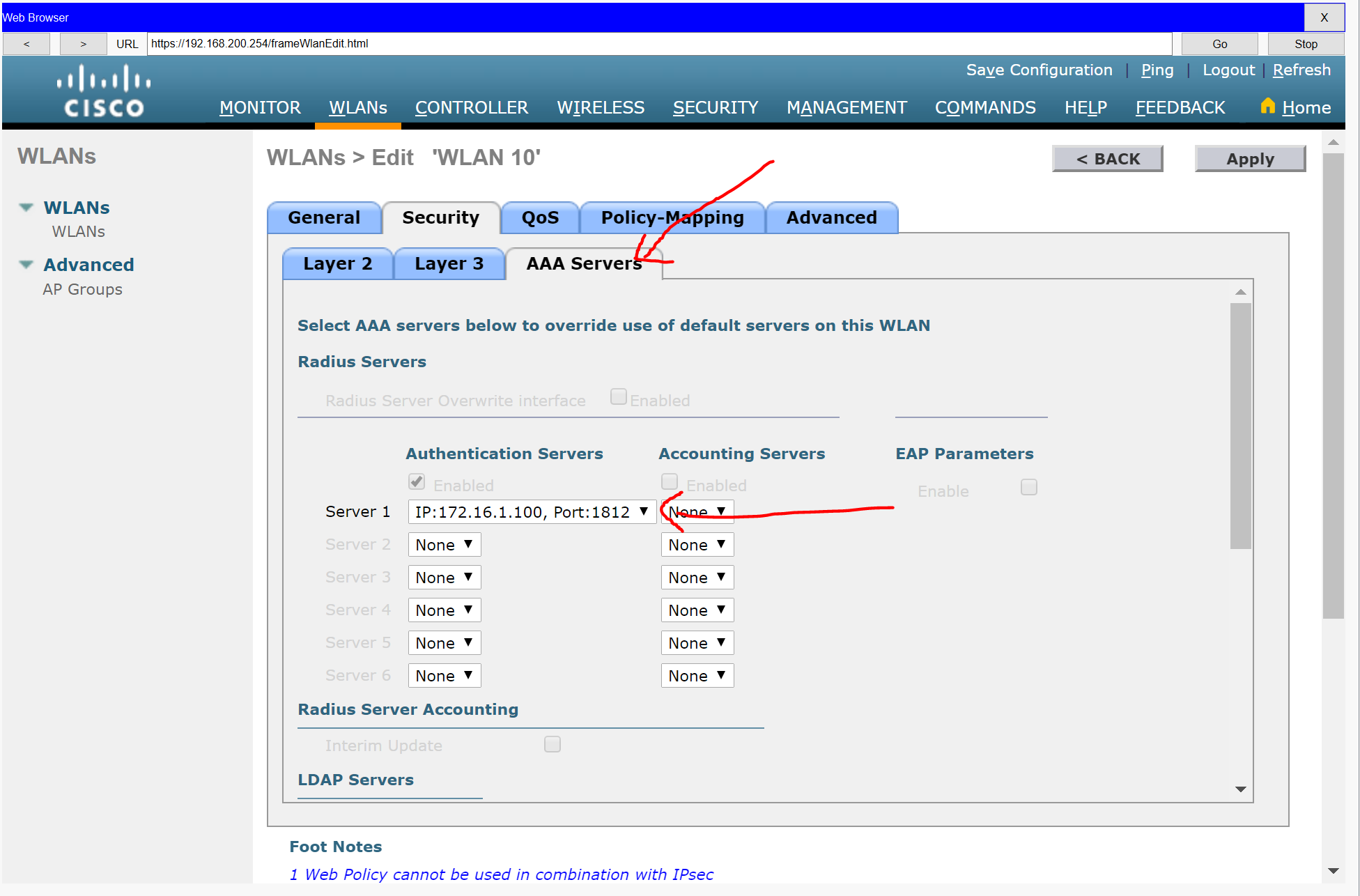
a. Configure the WLC with the RADIUS server IPv4 address
b. Use a shared secret of RADsecret.
Step 3: Configure a Wireless LAN.
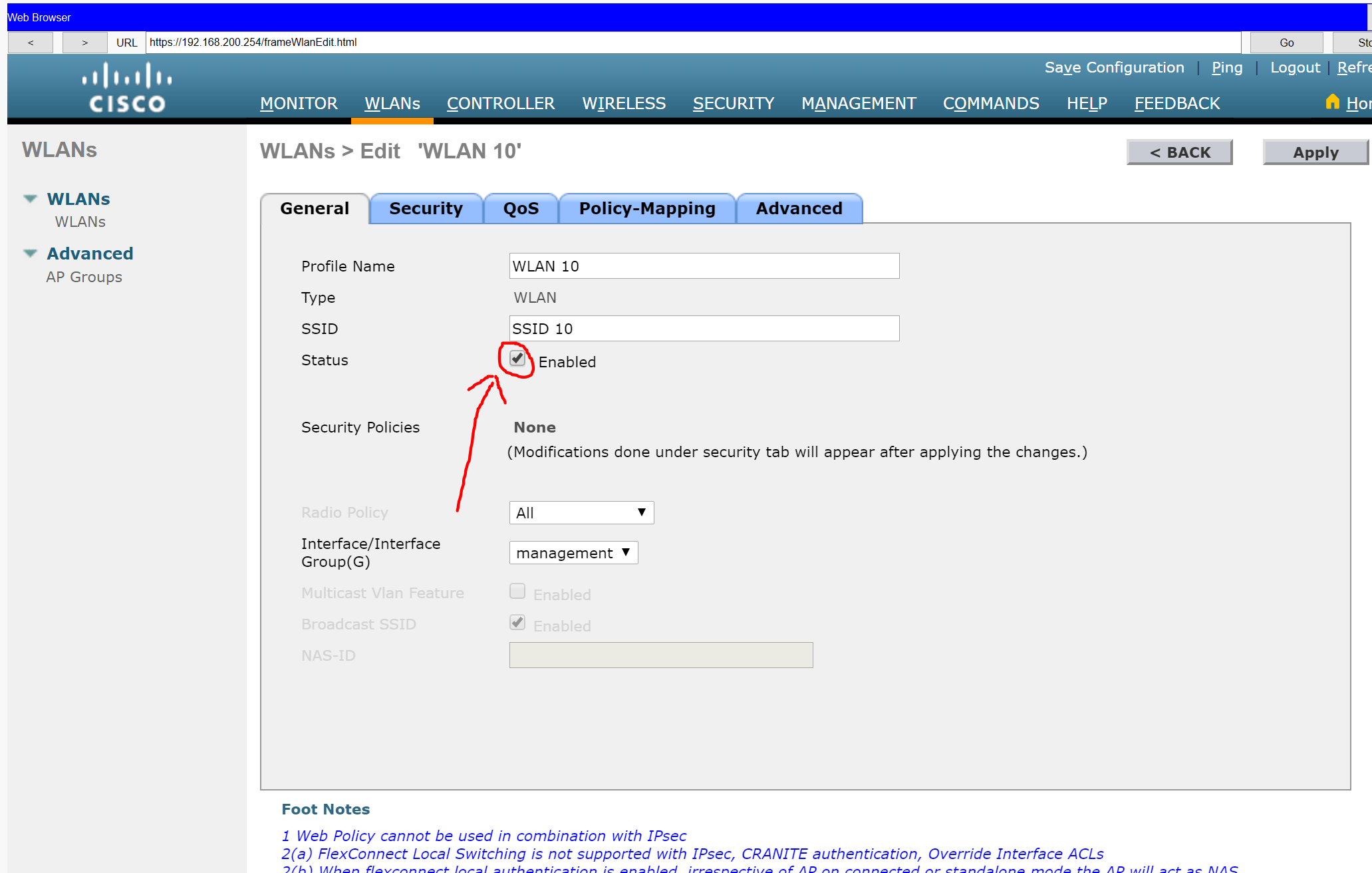
a. Create a new WLAN. Name it WLAN 10 and configure the SSID as SSID-10.
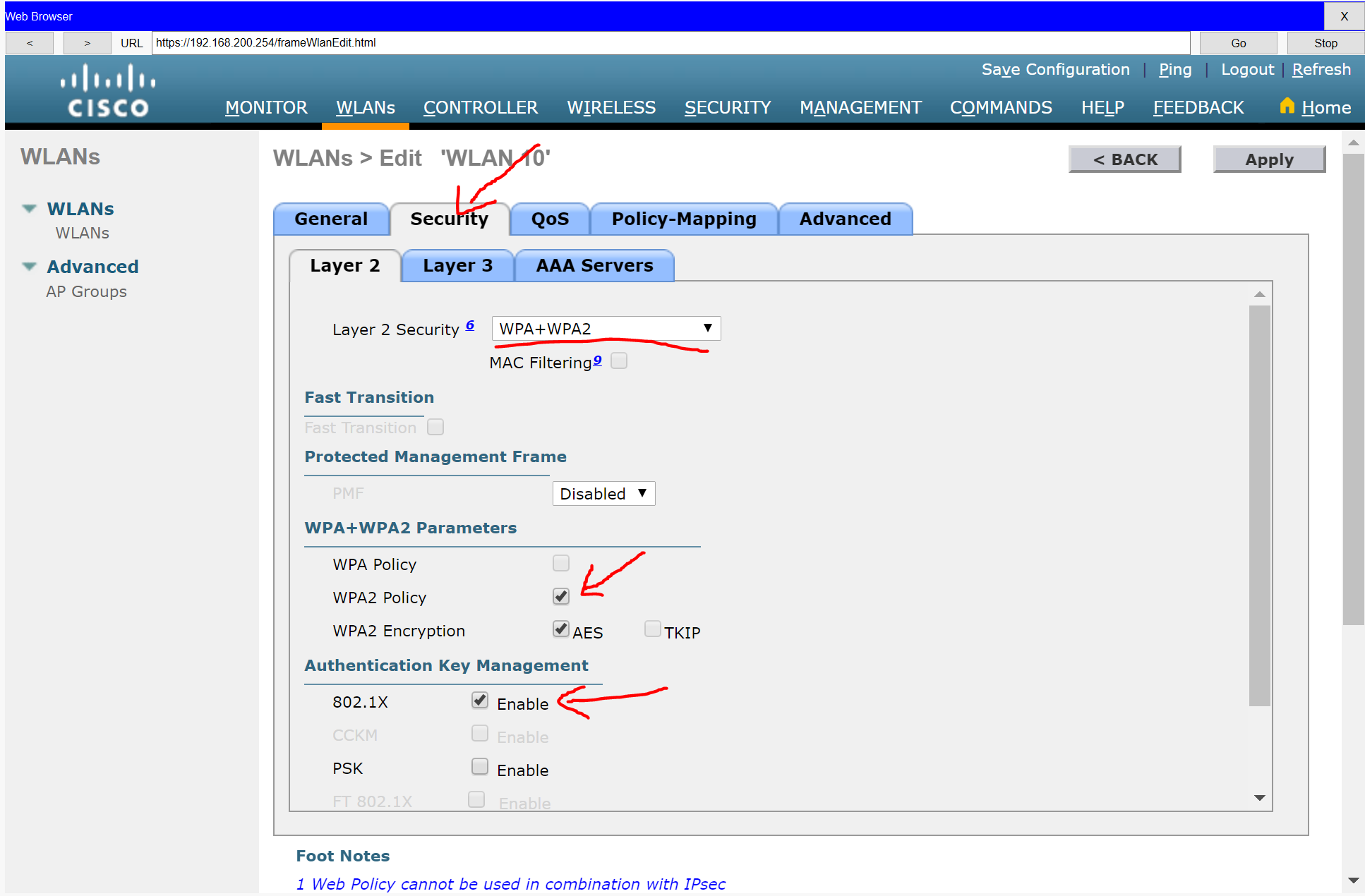
b. Configure the WLAN to use the WPA2 security policy and dot1x Authentication Key Management.
c. Configure the WLAN to use the RADIUS server that was previously configured to authenticate wireless users.
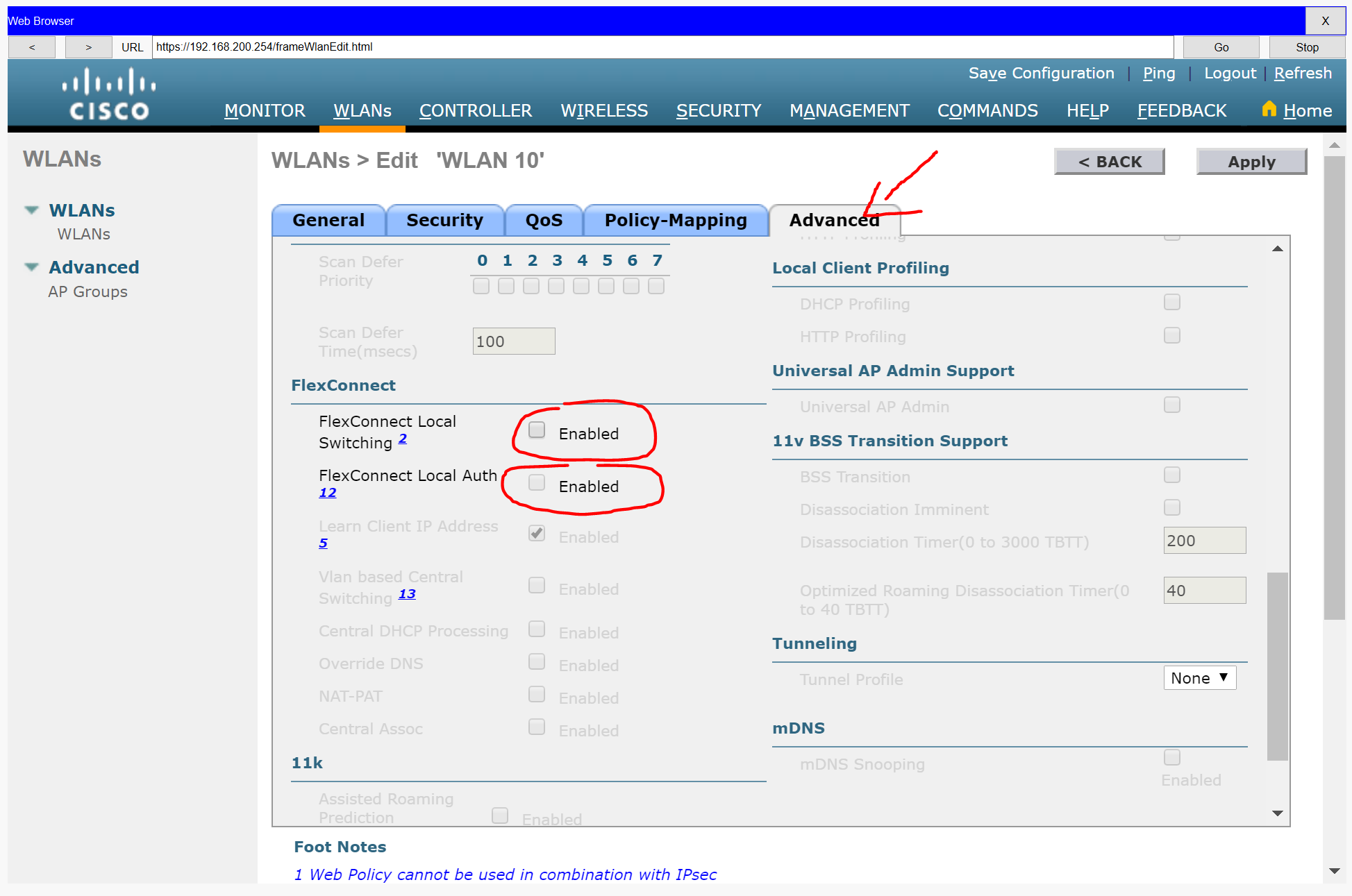
d. Open the Advanced tab and scroll down to the Flexconnect sections. Activate FlexConnect Local Switching and FlexConnect Local Auth.
e. Verify that the WLAN is configured and operational.
Step 4: Configure a DHCP scope for the management network.
Configure a new DHCP scope to be used by the LAPS and other management devices on the network.
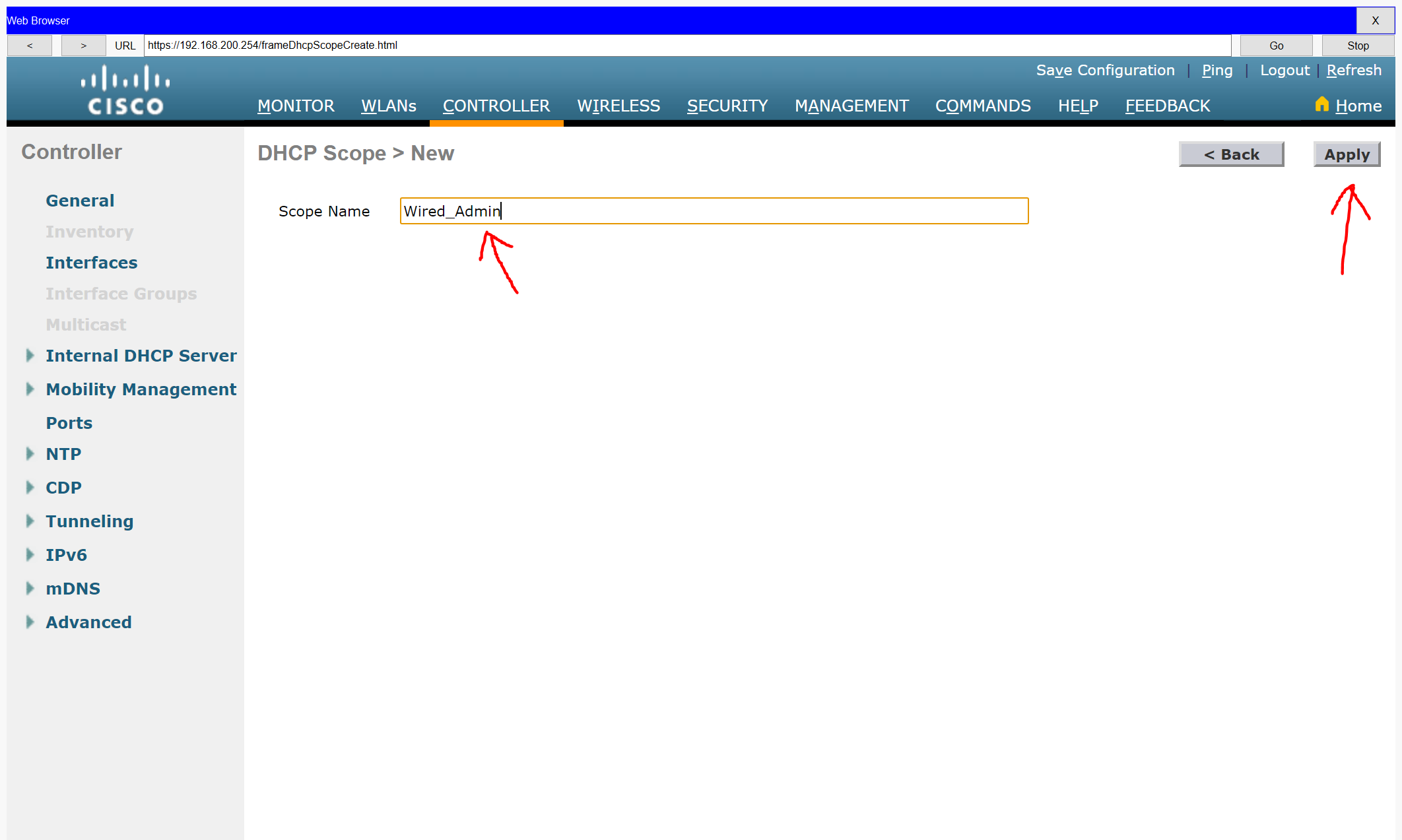
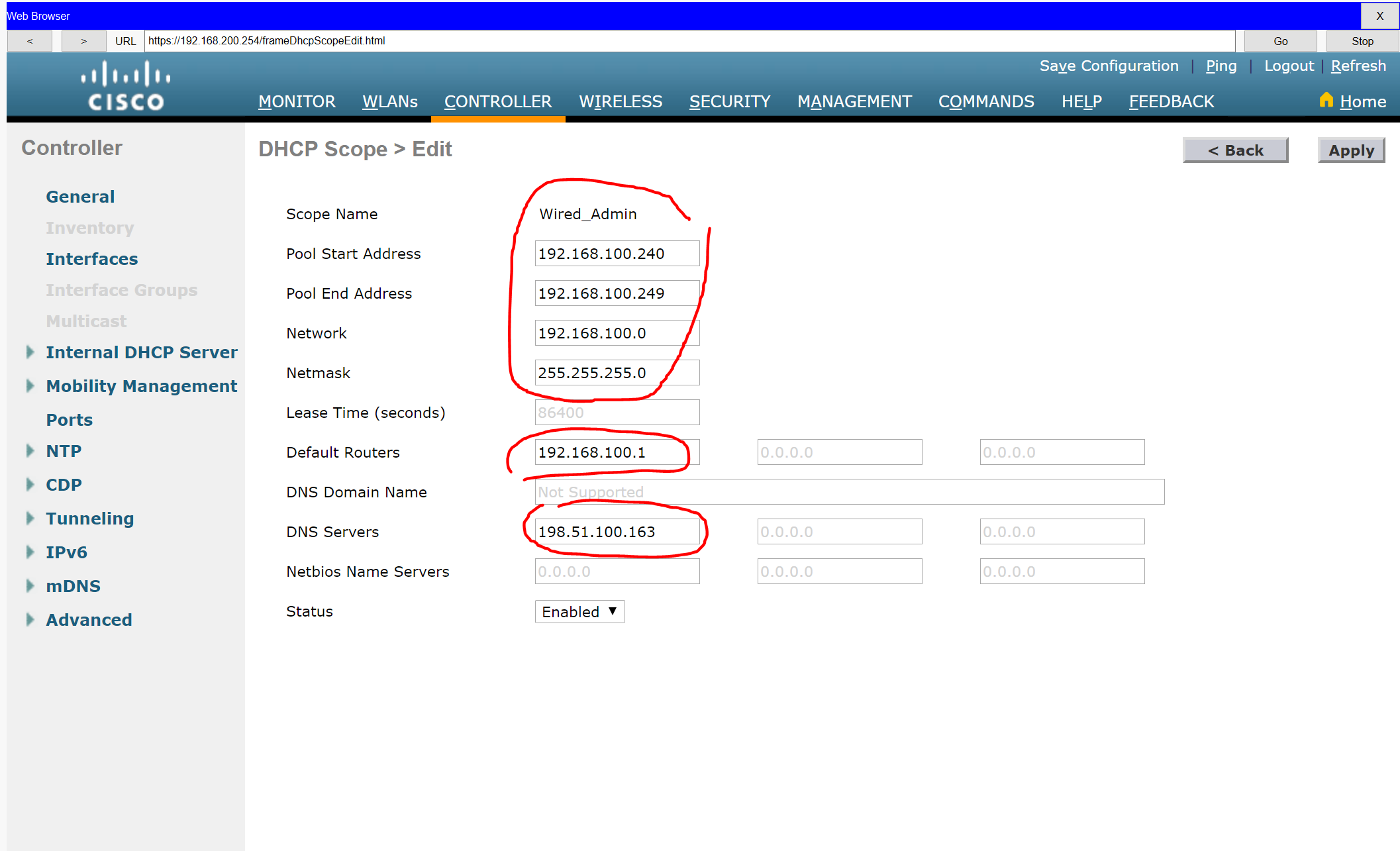
a. Name the DHCP scope Wired Admin.
b. Start the scope at address 192.168.100.240. End the scope at address 192.168.100.249.
c. Other information that is required can be found in the Addressing Table.
Step 5: Configure an SNMP server.
Configure an SNMP server to receive traps from the WLC.
a. Use the community name branch-wireless.
b. Use 172.16.1.100 as the server address.
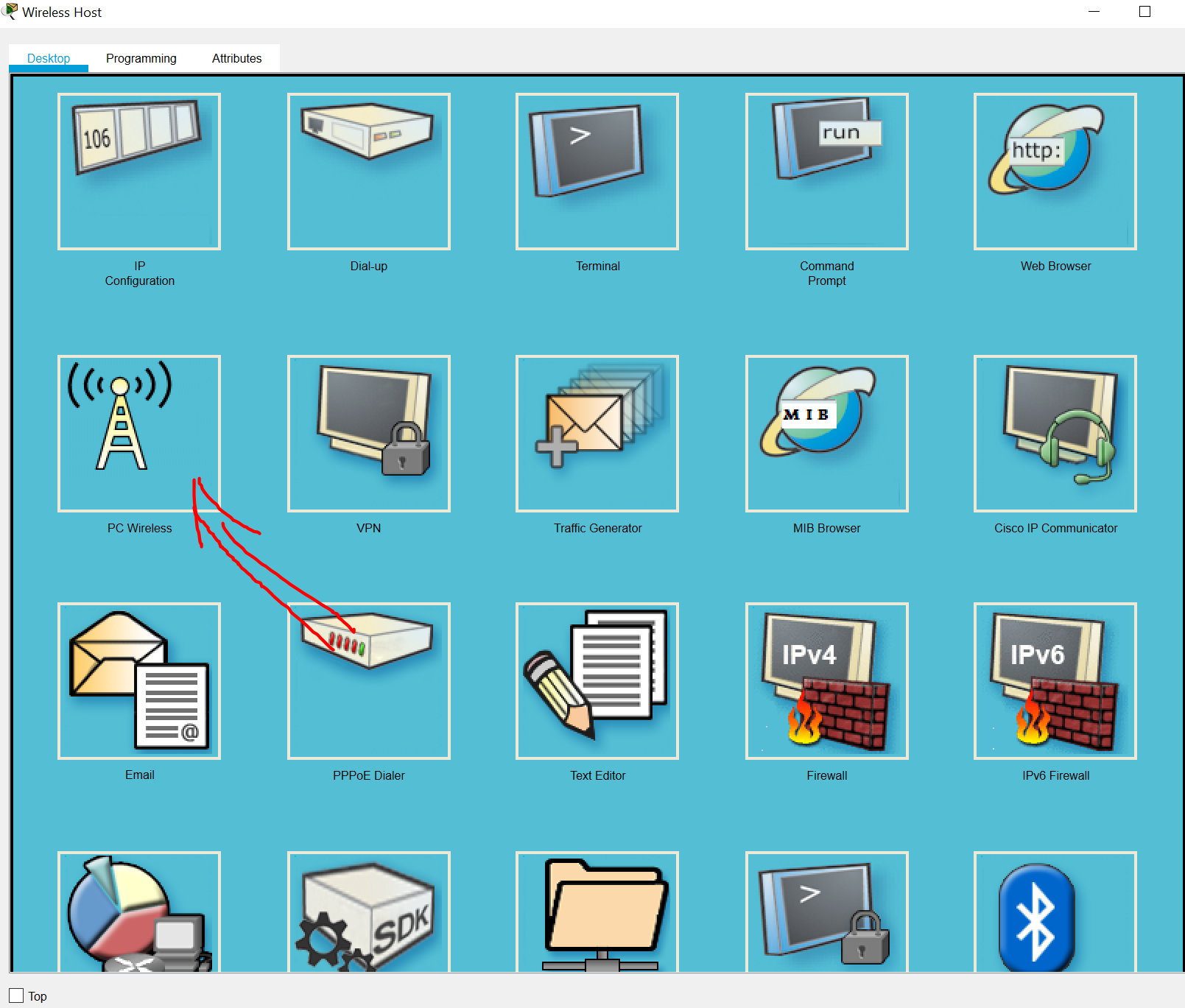
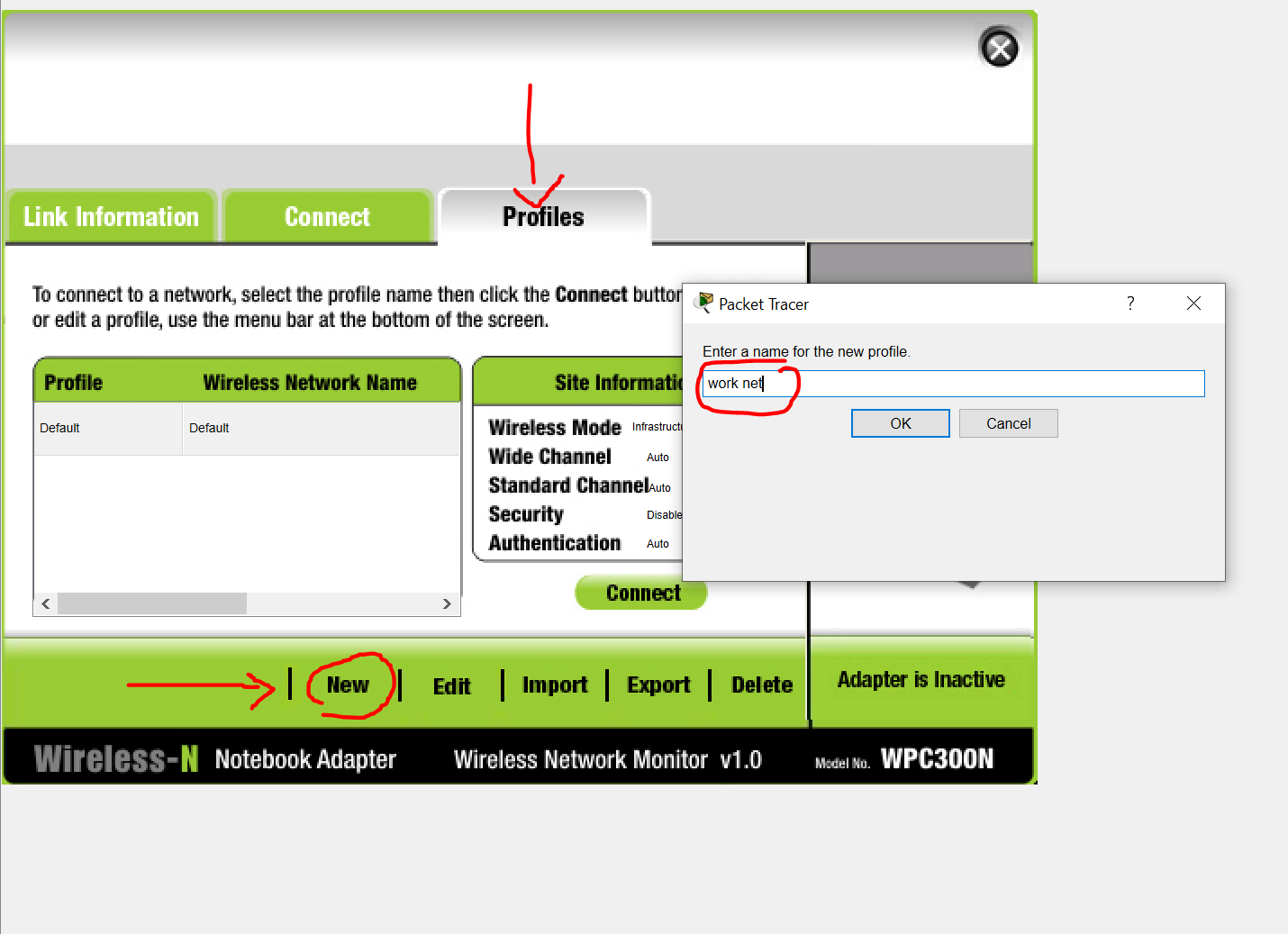
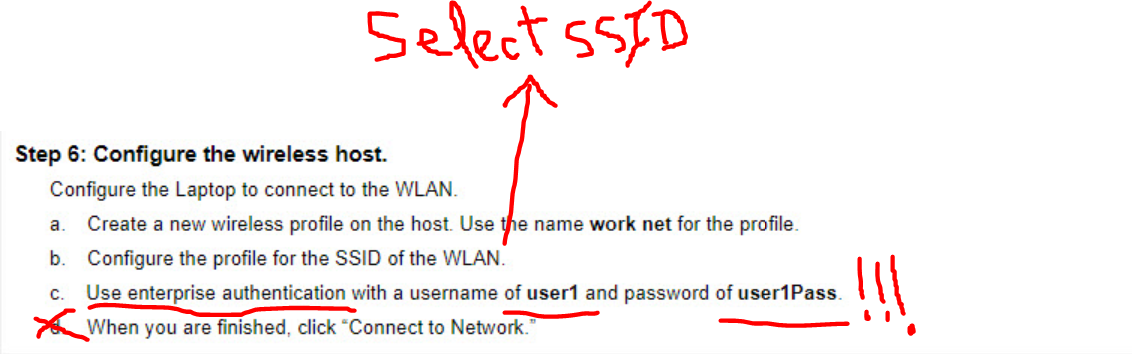
Step 6: Configure the wireless host.
Configure the Laptop to connect to the WLAN.
a. Create a new wireless profile on the host. Use the name work net for the profile.
b. Configure the profile for the SSID of the WLAN.
c. Use enterprise authentication with a username of user1 and password of user1Pass.
d. When you are finished, click “Connect to Network.”
Intructions – Answers
Part 1 + 2 + 3 (Instructions)
Sw-A Switch
en config t vlan 10 name users vlan 999 ununsed exit interface range f0/1-5, g0/1 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 10 interface range f0/1-5 switchport port-security switchport port-security maximum 4 switchport port-security violation restrict switchport port-security aging time 10 switchport port-security mac-address sticky exit interface f0/1 switchport port-security mac-address 00D0.D3DC.2825 exit ip dhcp snooping ip dhcp snooping vlan 10,999 interface range f0/1-5, g0/1 ip dhcp snooping limit rate 5 exit interface g0/1 ip dhcp snooping trust exit ip arp inspection vlan 10,999 interface g0/1 ip arp inspection trust exit interface range f0/1-5 spanning-tree portfast spanning-tree bpduguard enable interface range f0/6-24, g0/2 switchport mode access switchport access vlan 999 shutdown
Branch-101 Router
en config t interface g0/0/0.10 description WLAN users encapsulation dot1q 10 ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 exit ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.10.1 ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.10.254 ip dhcp pool WLAN-hosts network 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 192.168.10.1 dns-server 198.51.100.163 exit interface g0/0/1 ip address dhcp
Central Router
enable conf t ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 g0/0/2 ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/1/0 10 ipv6 route ::/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::2 ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:acad:b::2 10 ip route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 g0/0/2 ip route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 s0/1/0 10 ip route 192.168.3.122 255.255.255.255 s0/1/1 ipv6 route 2001:db8:acad:3::122/128 2001:db8:acad:d::2
Branch-101 Router
enable configure terminal ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 g0/0/1 ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/1/0 10 ipv6 route ::/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:C::1 ipv6 route ::/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::1 10
Part 4: Configure a Wireless LAN using a Wireless LAN Controller (Instructions)
Step 1: Configure a VLAN interface.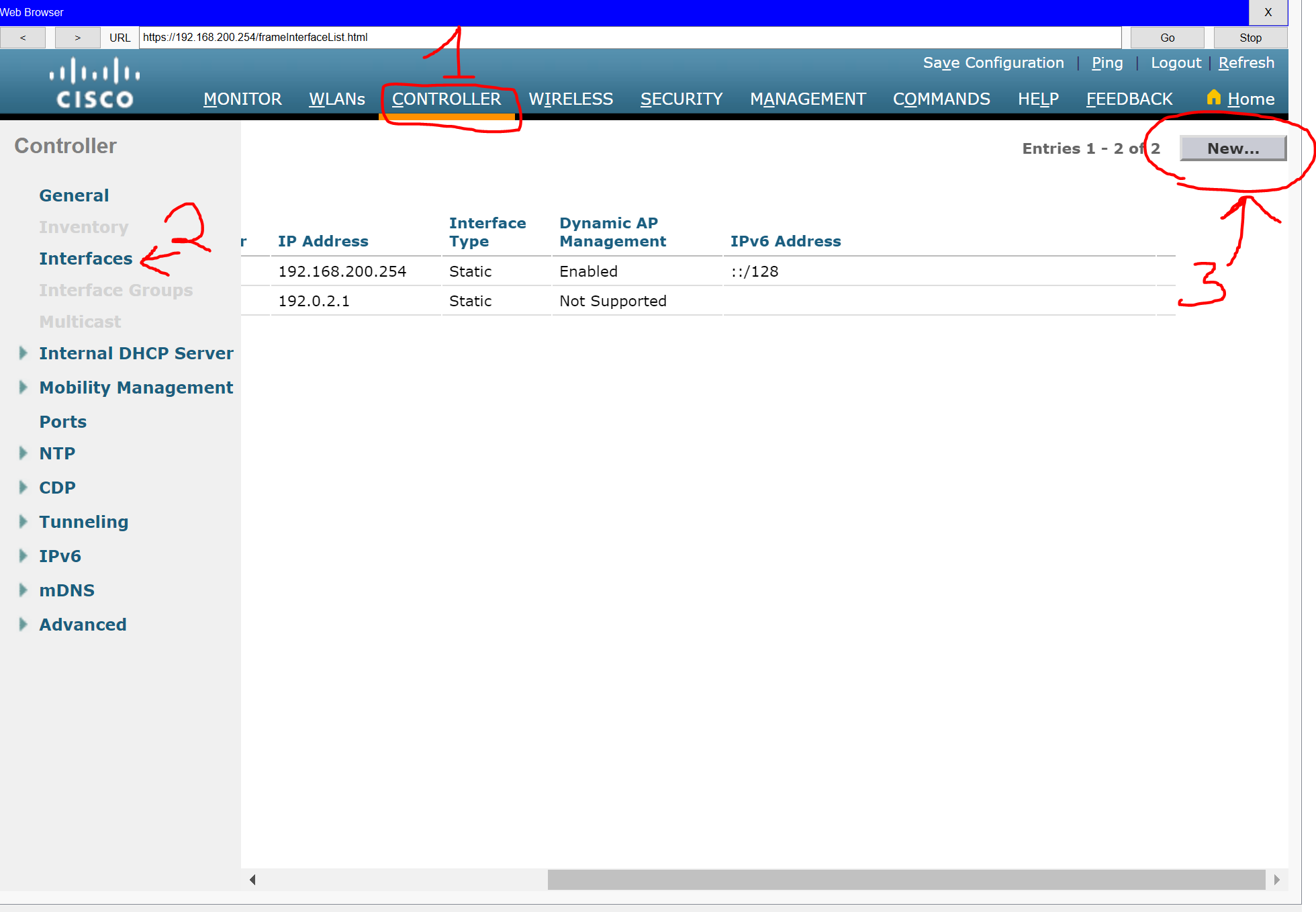
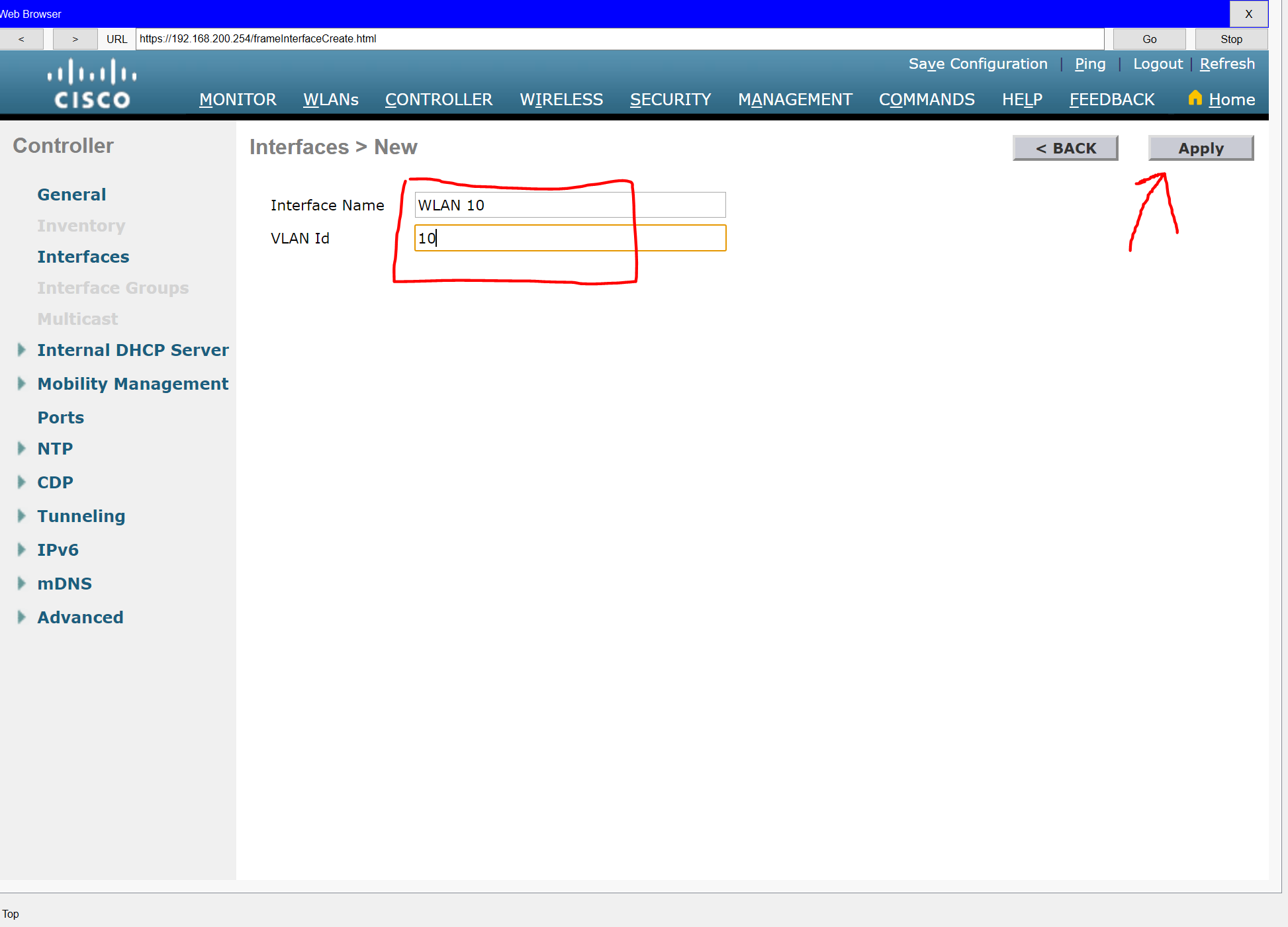
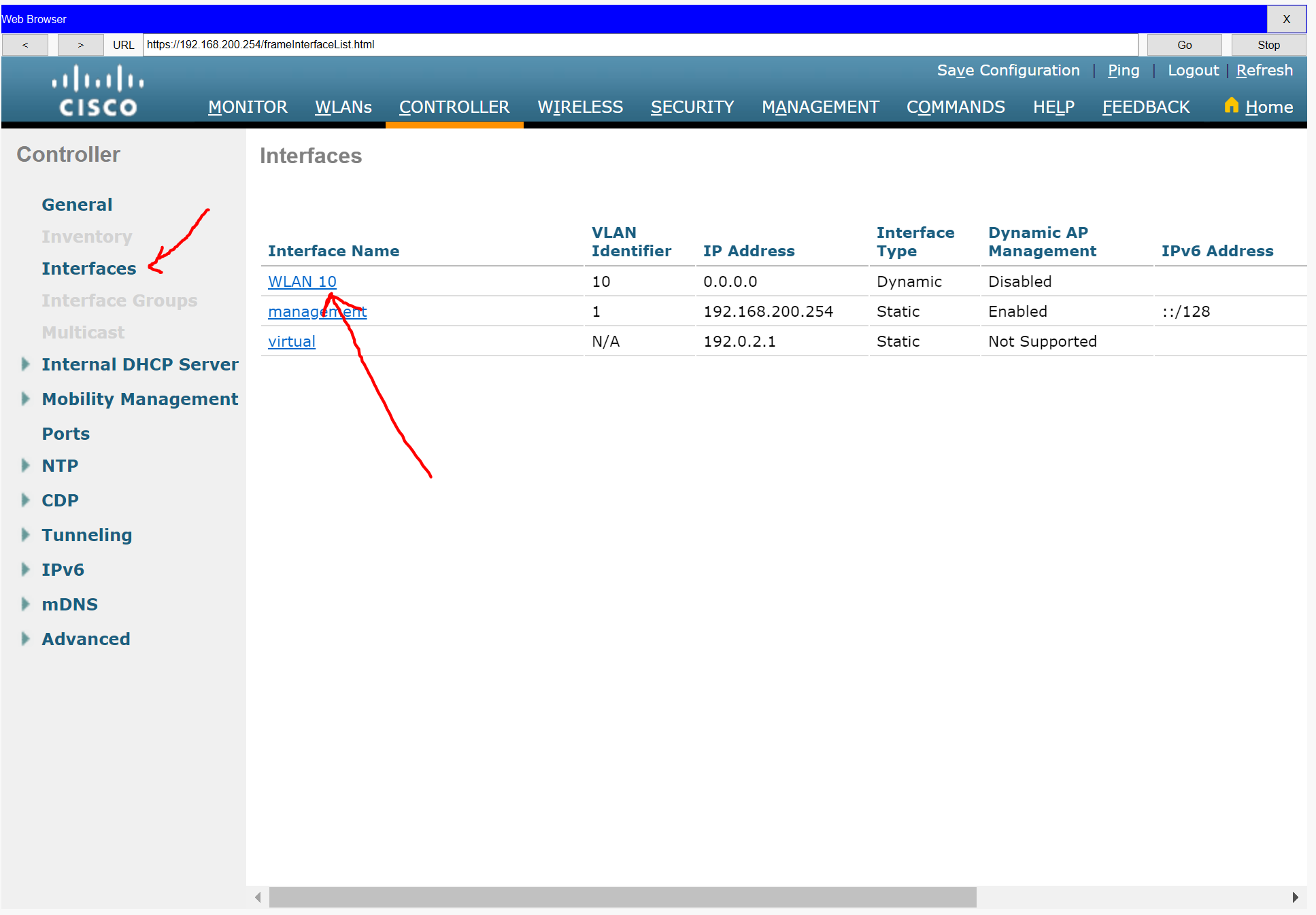
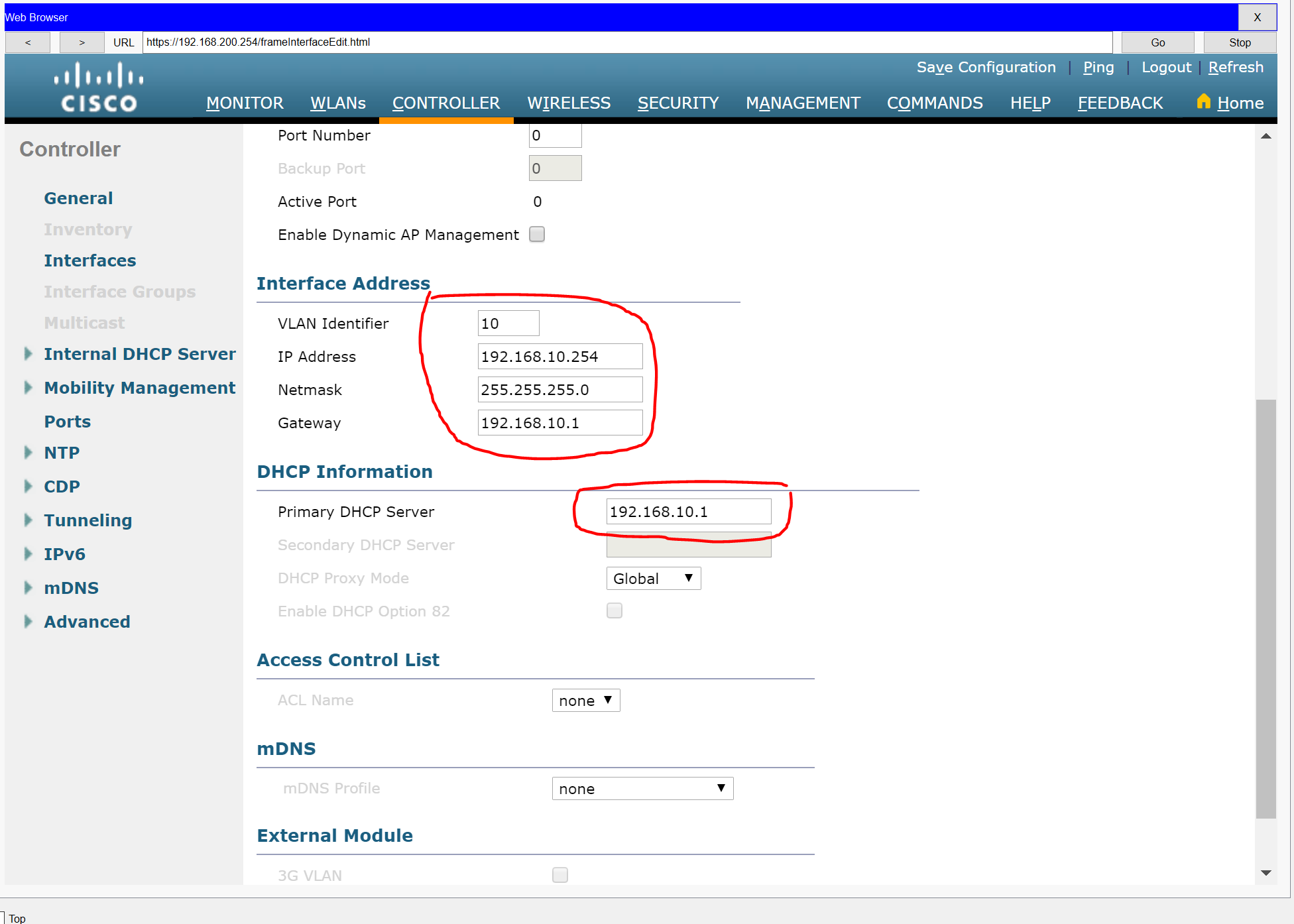



Step 2: Configure a RADIUS server.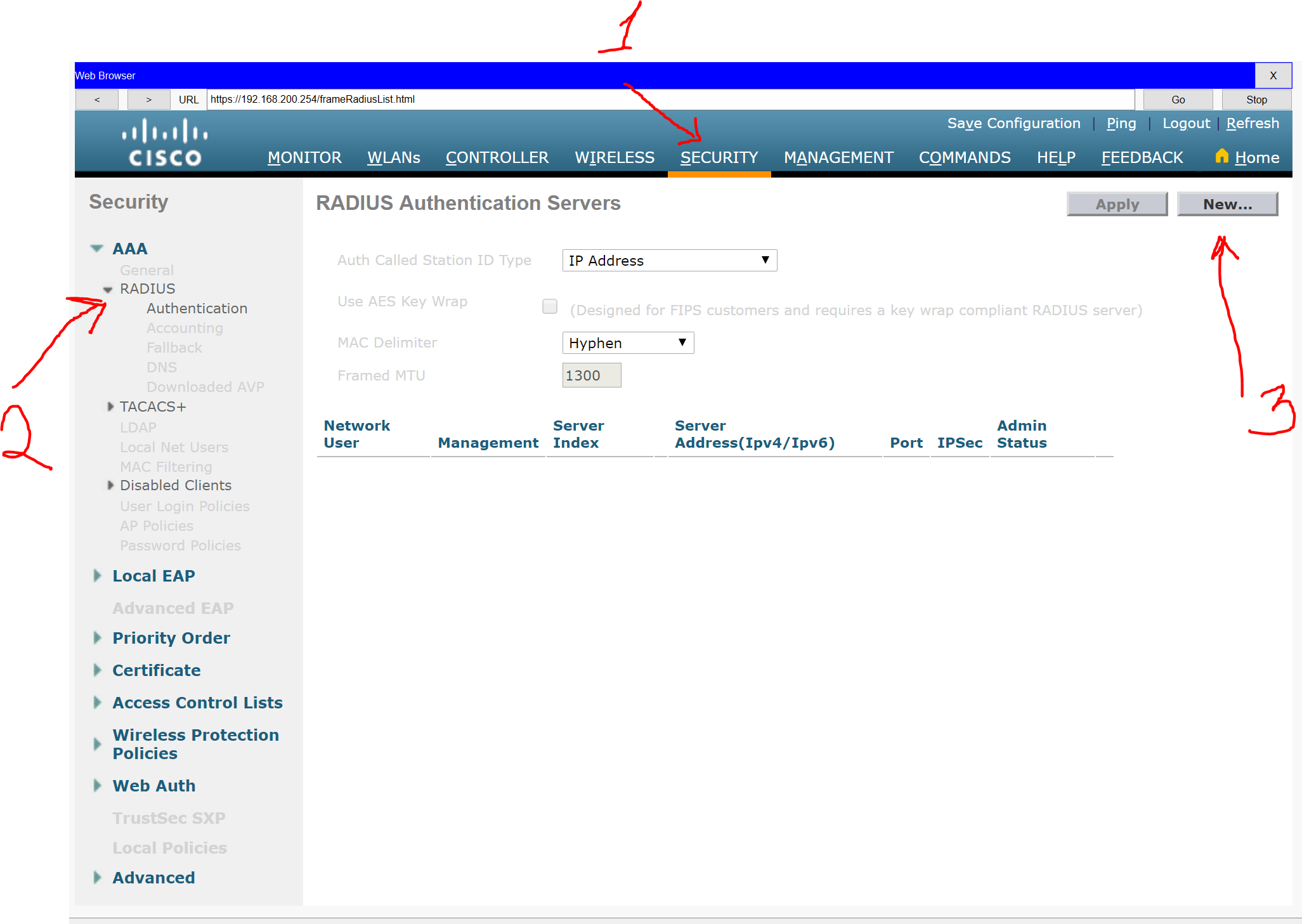
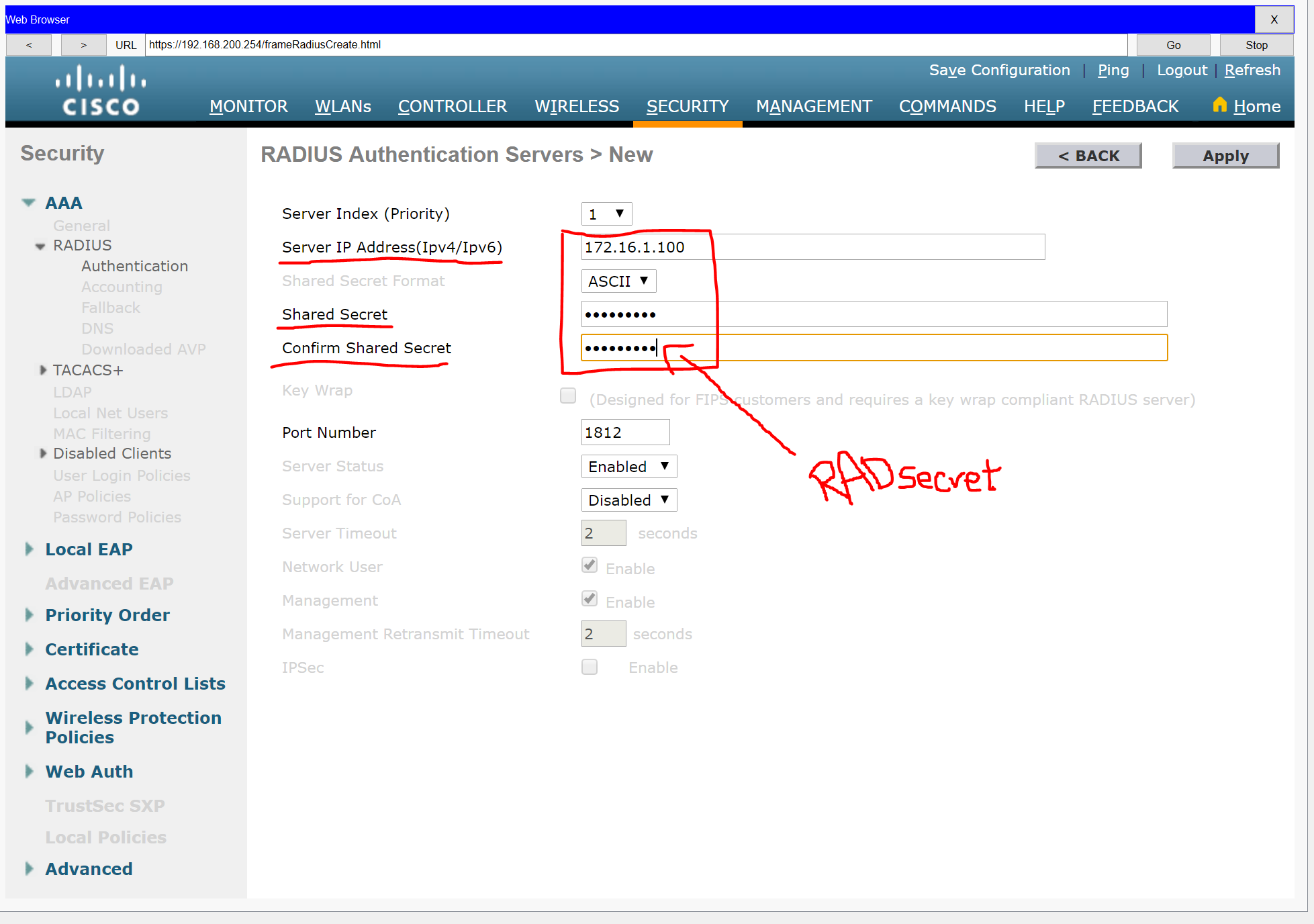

Step 3: Configure a Wireless LAN.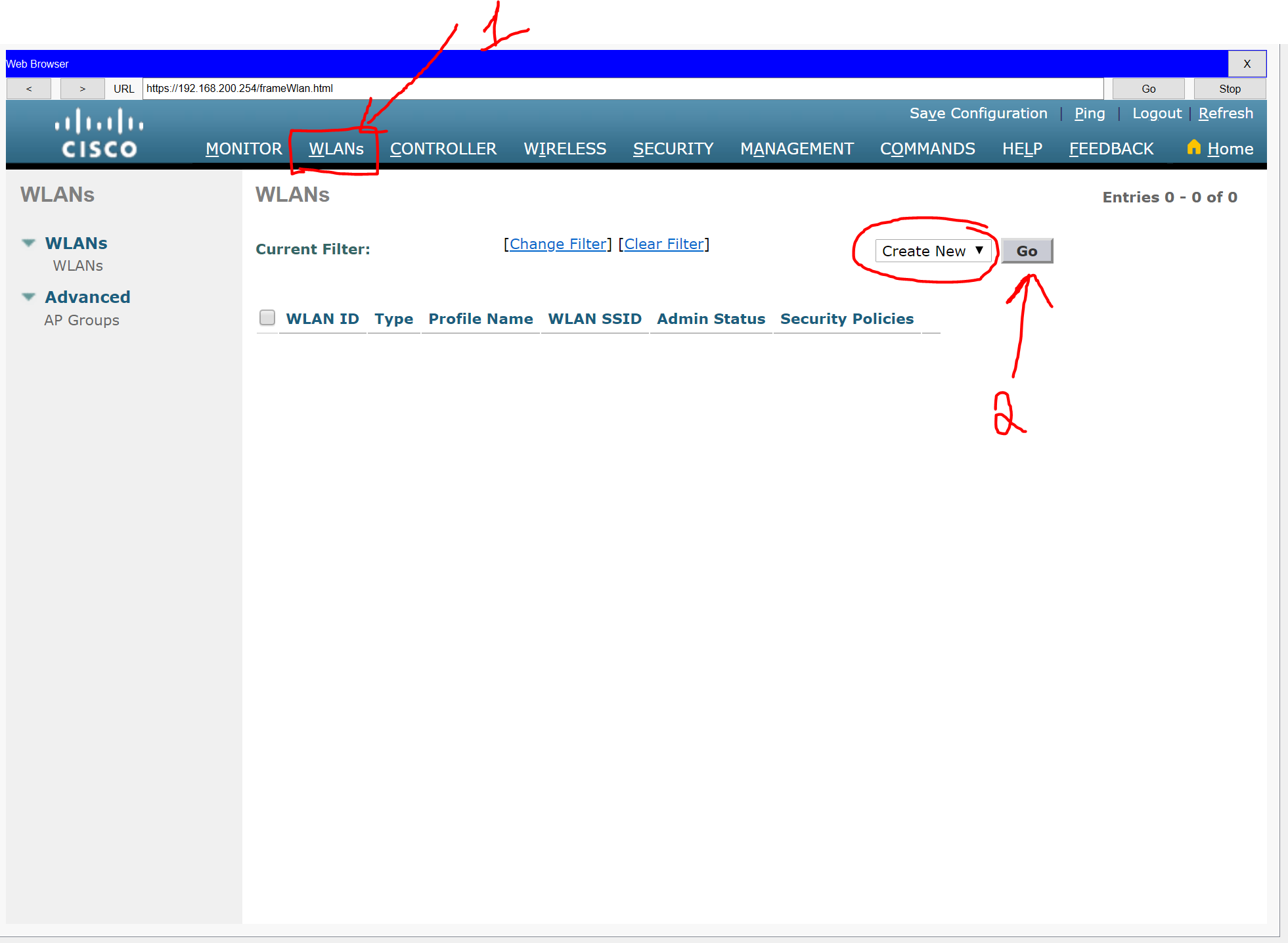
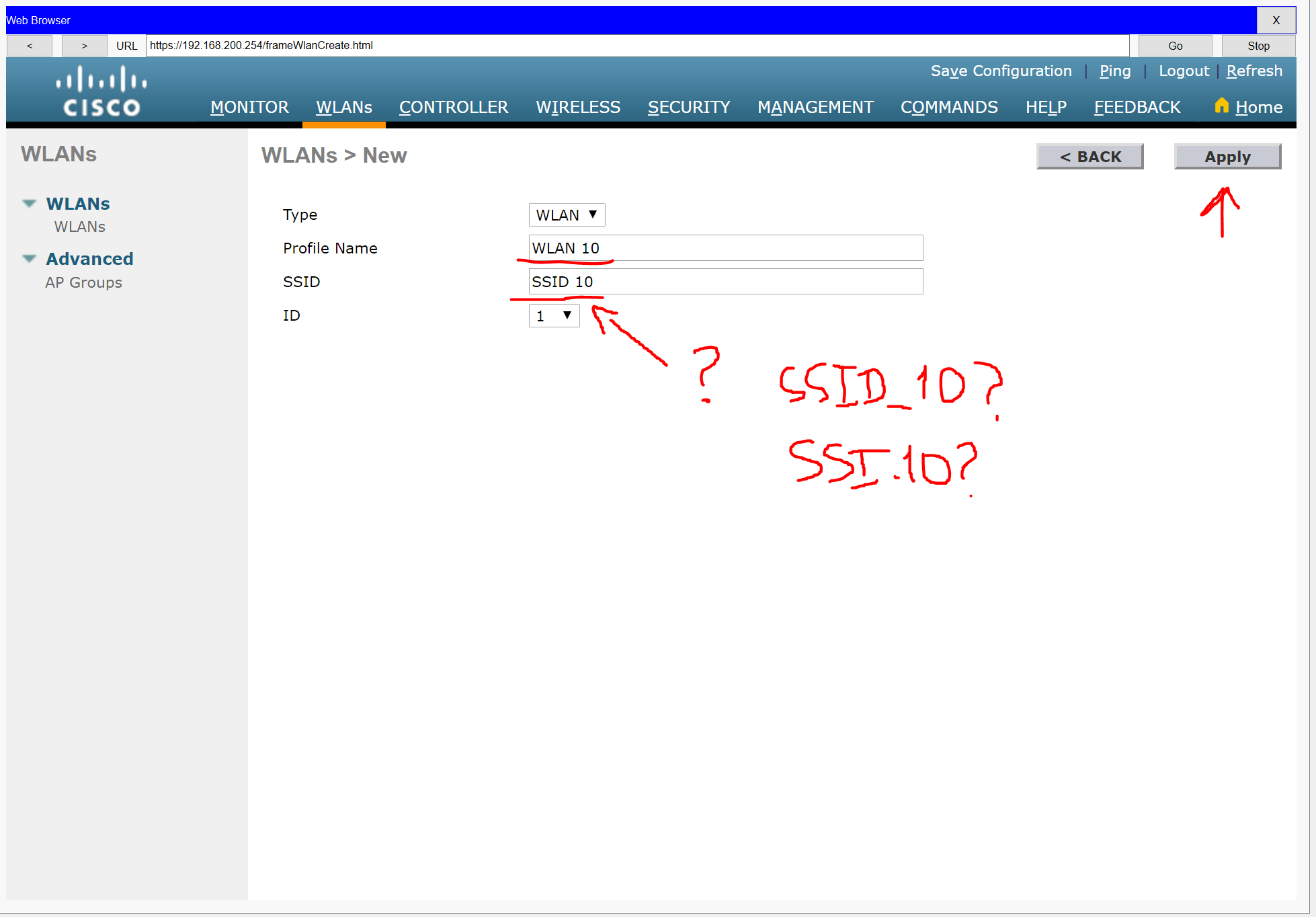





Step 4: Configure a DHCP scope for the management network.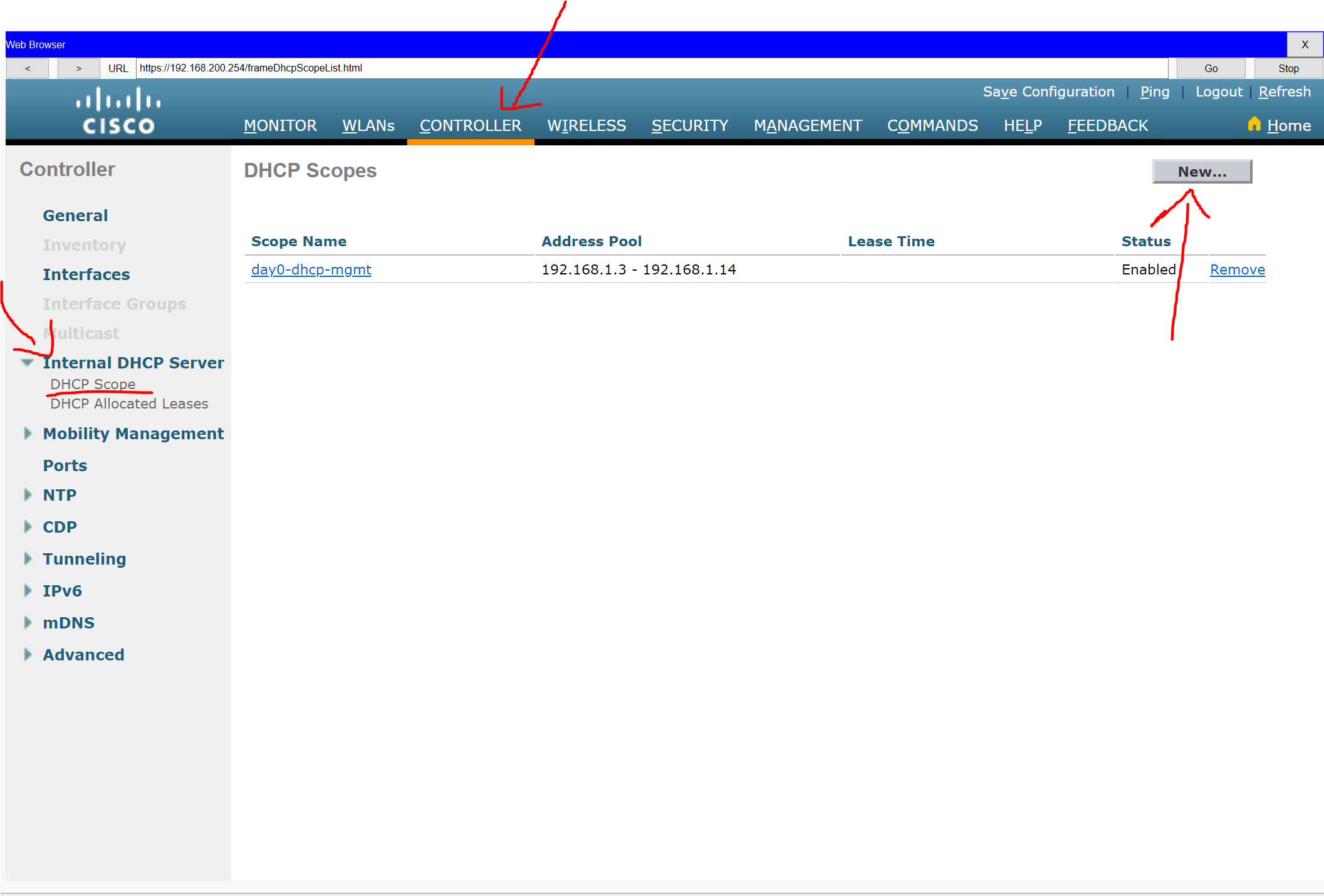



Step 5: Configure an SNMP server.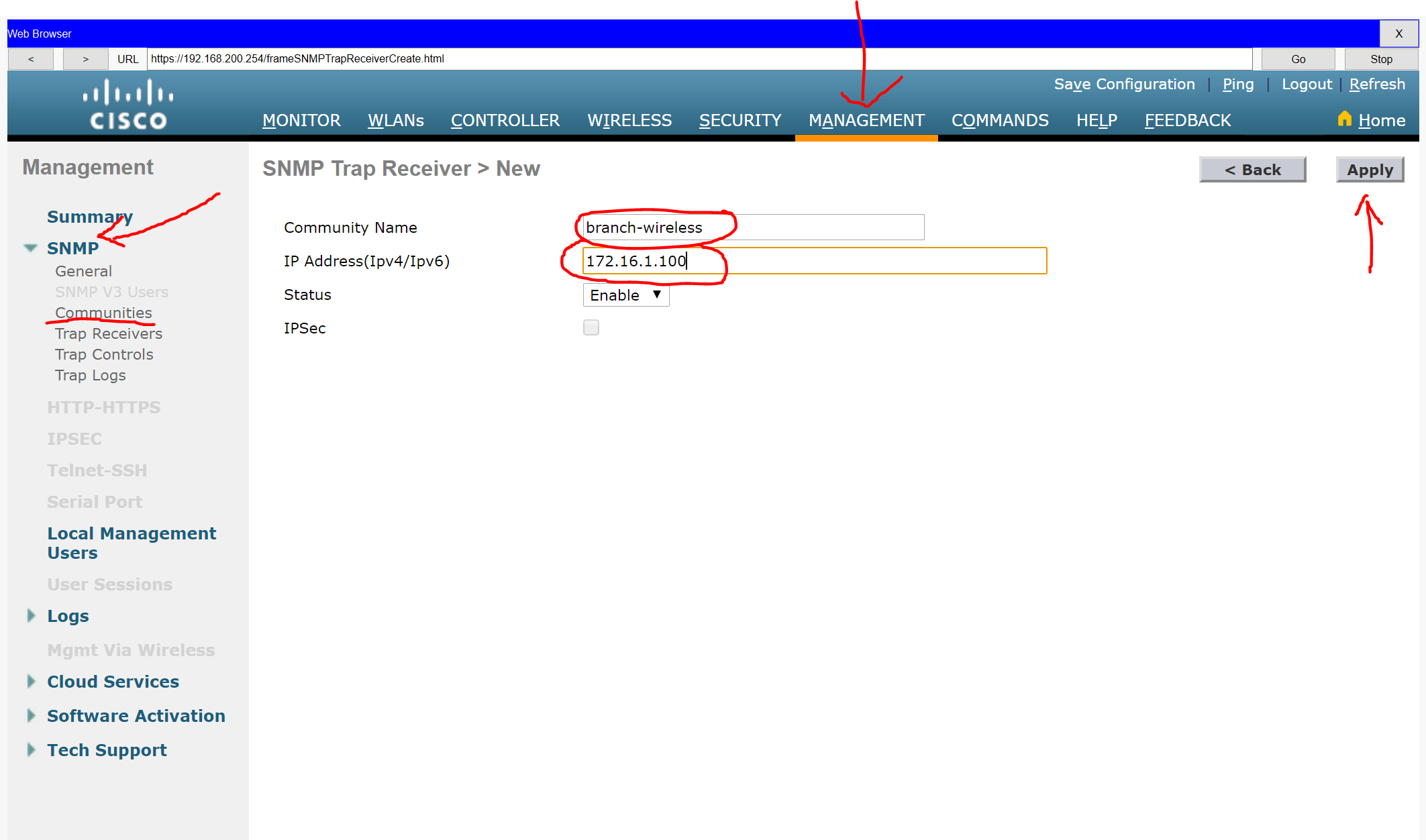
Step 6: Configure the wireless host.