CCNA 2 v5.0 Routing Protocols Chapter 5
1
Which command can be issued on a router to verify that automatic summarization is enabled?
Which command can be issued on a router to verify that automatic summarization is enabled?
show ip eigrp neighbors
show ip protocols*
show ip interface brief
show ip eigrp interfaces
2
Which address best summarizes the IPv6 addresses 2001:DB8:ACAD::/48, 2001:DB8:9001::/48, and 2001:DB8:8752::/49?
Which address best summarizes the IPv6 addresses 2001:DB8:ACAD::/48, 2001:DB8:9001::/48, and 2001:DB8:8752::/49?
2001:DB8:8000::/48
2001:DB8:8000::/36
2001:DB8:8000::/47
2001:DB8:8000::/34*
3
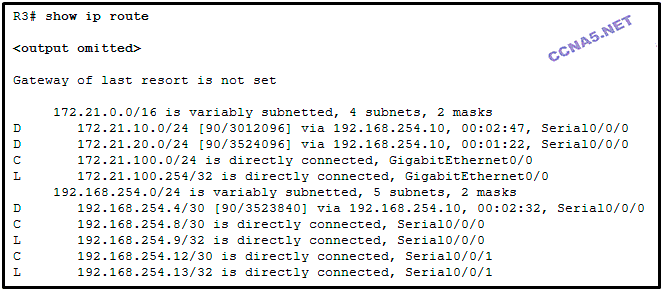
Refer to the exhibit. Router R3 is receiving multiple routes through the EIGRP routing protocol. Which statement is true about the implementation of summarization in this network?
Automatic summarization has been enabled only for the 172.21.100.0/24 network.
Automatic summarization is enabled on neighboring routers.
Automatic summarization is disabled on a per-interface basis.
Automatic summarization is disabled on R3.*
4

Refer to the exhibit. Considering that R2, R3, and R4 are correctly configured, why did R1 not establish an adjacency with R2, R3, and R4?
because the automatic summarization is enabled on R1
because the IPv4 address on Fa0/0 interface of R1 is incorrect
because the Fa0/0 interface of R1 is declared as passive for EIGRP*
because there is no network command for the network 192.168.1.0/24 on R1
5
In which IOS CLI mode must a network administrator issue the maximum-paths command to configure load balancing in EIGRP?
In which IOS CLI mode must a network administrator issue the maximum-paths command to configure load balancing in EIGRP?
router configuration mode*
interface configuration mode
global configuration mode
privileged mode
6
Two routers, R1 and R2, have established an EIGRP neighbor relationship, but there is still a connectivity problem. Which issue could be causing this problem?
Two routers, R1 and R2, have established an EIGRP neighbor relationship, but there is still a connectivity problem. Which issue could be causing this problem?
a process ID mismatch
an authentication mismatch
an access list that is blocking advertisements from other networks*
automatic summarization that is disabled on both routers
7

Refer to the exhibit. Remote users are experiencing connectivity problems when attempting to reach hosts in the 172.21.100.0 /24 network. Using the output in the exhibit, what is the most likely cause of the connectivity problem?
The GigabitEthernet 0/1 interface is not participating in the EIGRP process.*
The hello timer has been modified on interface GigabitEthernet 0/1 of R3 and not on the neighbor, causing a neighbor adjacency not to form.
The passive-interface command is preventing neighbor relationships on interface GigabitEthernet 0/0.
The GigabitEthernet interfaces are not limiting the flow of EIGRP message information and are being flooded with EIGRP traffic.
8
In which scenario will the use of EIGRP automatic summarization cause inconsistent routing in a network?
In which scenario will the use of EIGRP automatic summarization cause inconsistent routing in a network?
when there is no common subnet that exists between neighboring routers
when the routers in an IPv4 network have mismatching EIGRP AS numbers
when there is no adjacency that is established between neighboring routers
when the routers in an IPv4 network are connected to discontiguous networks with automatic summarization enabled*
9

Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1 and R2 are directly connected via their serial interfaces and are both running the EIGRP routing protocol. R1 and R2 can ping the directly connected serial interface of their neighbor, but they cannot form an EIGRP neighbor adjacency.
What action should be taken to solve this problem?
Configure the same hello interval between the routers.
Configure EIGRP to send periodic updates.
Enable the serial interfaces of both routers.
Configure both routers with the same EIGRP process ID.*
10

Refer to the exhibit. Which statement accurately reflects the configuration of routing on the HQ router?
The IP address assigned to the GigabitEthernet0/0 interface is 172.16.2.0 255.255.255.0.
A static default route was configured on this router.*
A static default route was learned via EIGRP routing updates.
The static default route should be redistributed using the default-information originate command.
11
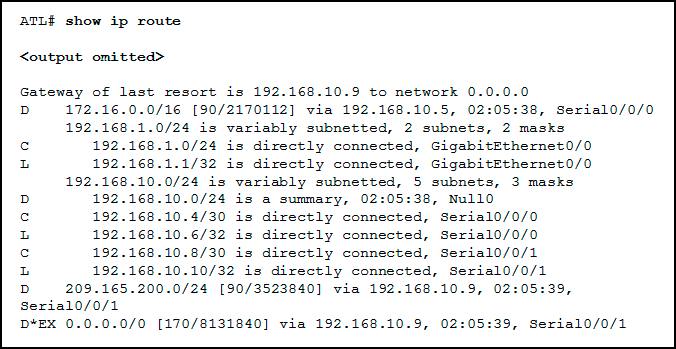
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is supported by the output?
The route to 192.168.1.1 represents the configuration of a loopback interface.
A static default route has been manually configured on this router.
A default route is being learned through an external process.*
Summarization of routes has been manually configured.
12
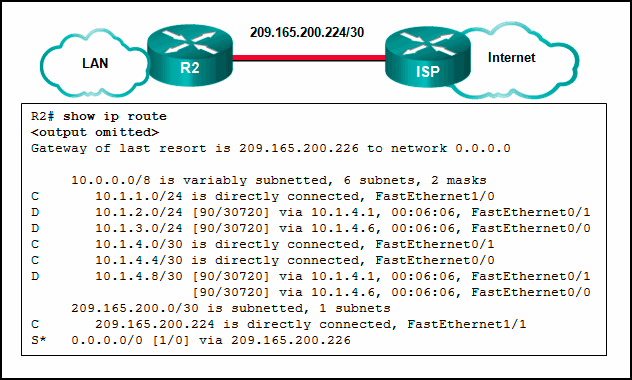
Refer to the exhibit. Which two routes will be advertised to the router ISP if autosummarization is disabled? (Choose two.)
10.1.2.0/24*
10.1.4.0/28
10.1.4.0/30*
10.1.4.0/24
10.1.0.0/16
13

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured EIGRP authentication between routers R1 and R2. After the routing tables are reviewed, it is noted that neither router is receiving EIGRP updates. What is a possible cause for this failure?
The same autonomous system numbers must be used in the interface configurations of each router.*
The key string should be used in interface mode instead of the key chain.
The same number of key strings must be used on each router.
The same key chain name must be used on each router.
The authentication configuration is correct, issue the show ip eigrp neighbors command to troubleshoot the issue.
14
Two routers, R1 and R2, share a 64 kb/s link. An administrator wants to limit the bandwidth used by EIGRP between these two routers to 48 kb/s. Which command is used on both routers to configure the new bandwidth setting?
Two routers, R1 and R2, share a 64 kb/s link. An administrator wants to limit the bandwidth used by EIGRP between these two routers to 48 kb/s. Which command is used on both routers to configure the new bandwidth setting?
ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 100 48
ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 100 75*
ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 75 100
ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 64 48
ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 100 64
15
Which three statements are advantages of using automatic summarization? (Choose three.)
Which three statements are advantages of using automatic summarization? (Choose three.)
It decreases the number of entries in the routing table.*
It reduces the frequency of routing updates.*
It ensures that traffic for multiple subnets uses one path through the internetwork.*
It maximizes the number of routes in the routing table.
It improves reachability in discontiguous networks.
It increases the size of routing updates.
16
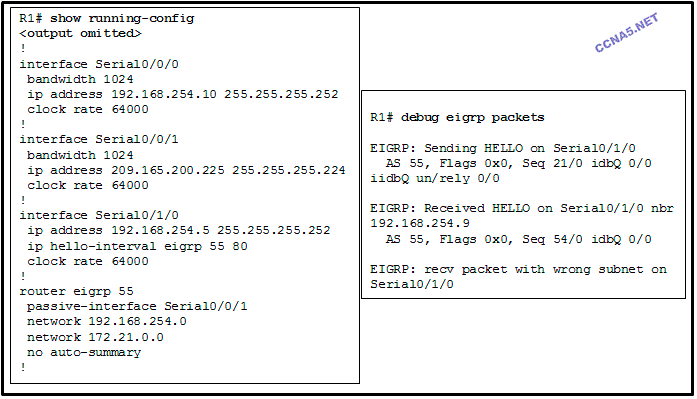
Refer to the exhibit. After the configuration shown is applied on router R1, the exhibited status message is displayed. Router R1 is unable to form a neighbor relationship with R2 on the serial 0/1/0 interface. What is the most likely cause of this problem?
The passive-interface command should have been issued on serial 0/1/0.
The IPv4 address configured on the neighbor that is connected to R1 serial 0/1/0 is incorrect.*
The hello interval has been altered on serial 0/1/0 and is preventing a neighbor relationship from forming.
The network statement used for EIGRP 55 does not enable EIGRP on interface serial 0/1/0.
The networks that are configured on serial 0/0/0 and serial 0/1/0 of router R1 are overlapping.
17
What is a characteristic of manual route summarization?
What is a characteristic of manual route summarization?
requires high bandwidth utilization for the routing updates
has to be configured globally on the router
reduces total number of routes in routing tables*
cannot include supernet routes
18
Fill in the blank. Do not use abbreviations.
The ” passive-interface ” command causes an EIGRP router to stop sending hello packets through an interface.
Fill in the blank. Do not use abbreviations.
The ” passive-interface ” command causes an EIGRP router to stop sending hello packets through an interface.
19

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has issued the shown commands. The EIGRP routing domain has completely converged and a network administrator is planning on configuring EIGRP authentication throughout the complete network. On which two interfaces should EIGRP authentication be configured between R2 and R3? (Choose two.)
gig 0/0 of R3
serial 0/1/0 of R4
serial 0/1/0 of R2*
serial 0/0/1 of R2
serial 0/0/1 of R3*
20
Fill in the blank. Do not use abbreviations.
What is the command that should be issued on a router to verify that EIGRP adjacencies were formed?
Fill in the blank. Do not use abbreviations.
What is the command that should be issued on a router to verify that EIGRP adjacencies were formed?
” show ip eigrp neighbor ”
21

Launch PT Hide and Save PT
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
R1 and R2 could not establish an EIGRP adjacency. What is the problem?
EIGRP is down on R2.
EIGRP is down on R1.*
R1 Fa0/0 link local address is wrong.
R1 Fa0/0 and R2 Fa0/0 are on different networks.
R1 Fa0/0 is not configured to send hello packets.
22

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has attempted to implement a default route from R1 to the ISP and propagate the default route to EIGRP neighbors. Remote connectivity from the EIGRP neighbor routers to the ISP connected to R1 is failing. Based on the output from the exhibit, what is the most likely cause of the problem?
There are no EIGRP neighbor relationships on R1.
The command default-information originate has not been issued on R1.
The network statement for the ISP connection has not been issued.
The command redistribute static has not been issued on R1.*
The ip route command must specify a next-hop IP address instead of an exit interface when creating a default route.
23
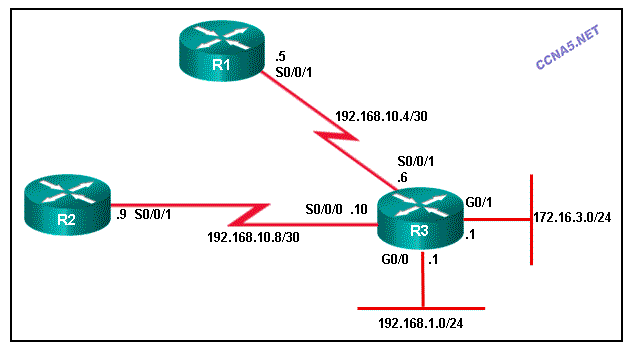
Refer to the exhibit. All networks are active in the same EIGRP routing domain. When the auto-summary command is issued on R3, which two summary networks will be advertised to the neighbors? (Choose two.)
172.16.3.0/24
172.16.0.0/16*
192.168.10.0/24*
192.168.10.0/30
192.168.1.0/30